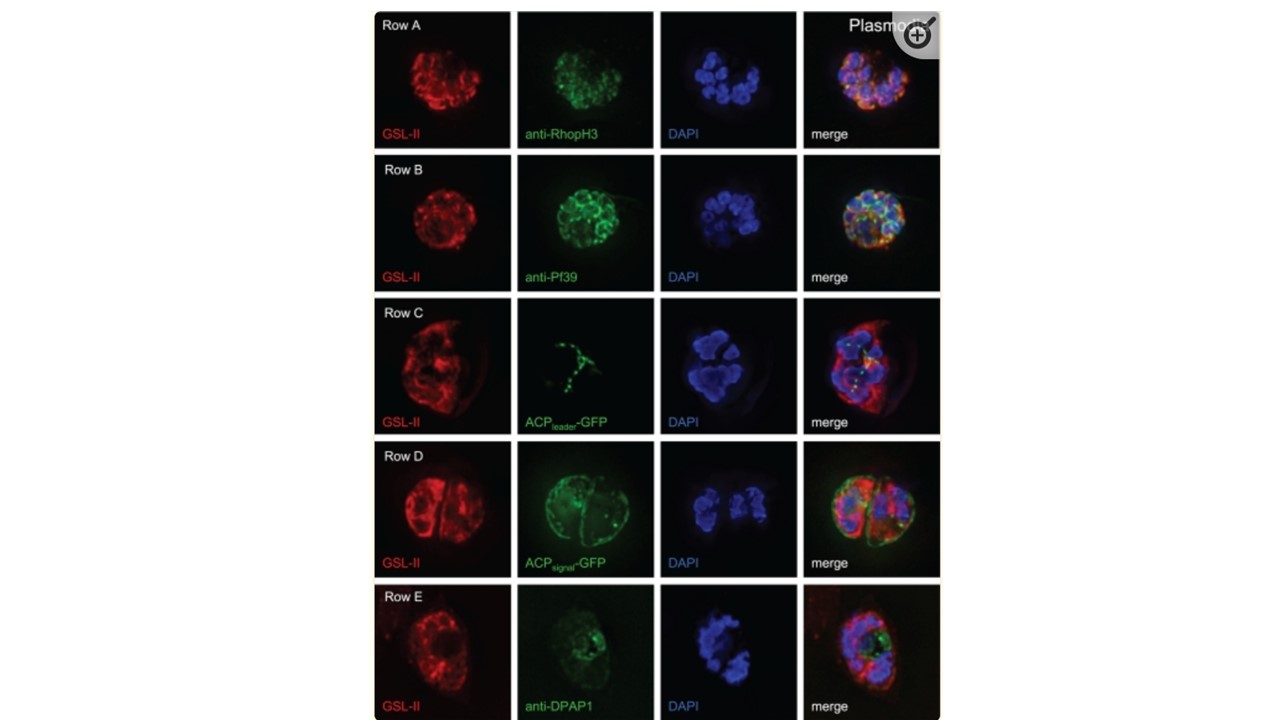
Deconvolving micrographs of Plasmodium-infected RBCs show that GSL-II, which binds to Plasmodium N-glycans, colocalizes with rhoptries (row A) and the ER (row B) but does not colocalize with apicoplasts (row C), the parasitophorous vacuole (row D), or the food vacuole (row E). In each case GSL-II is labeled red with Alexafluor 594, while antibodies labeled green with Alexafluor 488 are against RhopH3 (rhoptries), Pf39 (ER), and food vacuole (DPAP1) (14, 30, 51). Alternatively, GFP is targeted to apicoplasts (ACPleader-GFP) and the parasitophorous vacuole (ACPsignal-GFP) (55). Control experiments with anti-GFP antibodies show that both apicoplasts and parasitophorous vacuoles are accessible to exogenous probes.
Bushkin GG, Ratner DM, Cui J, Banerjee S, Duraisingh MT, Jennings CV, DvorinJD, Gubbels MJ, Robertson SD, Steffen M, O'Keefe BR, Robbins PW, Samuelson J. Suggestive evidence for Darwinian Selection against asparagine-linked glycans of Plasmodium falciparum and Toxoplasma gondii. Eukaryot Cell. 2010 9(2):228-41. PMID: 19783771
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0208500 | acyl carrier protein |
| PF3D7_0905400 | high molecular weight rhoptry protein 3 |
| PF3D7_1108600 | endoplasmic reticulum-resident calcium binding protein |