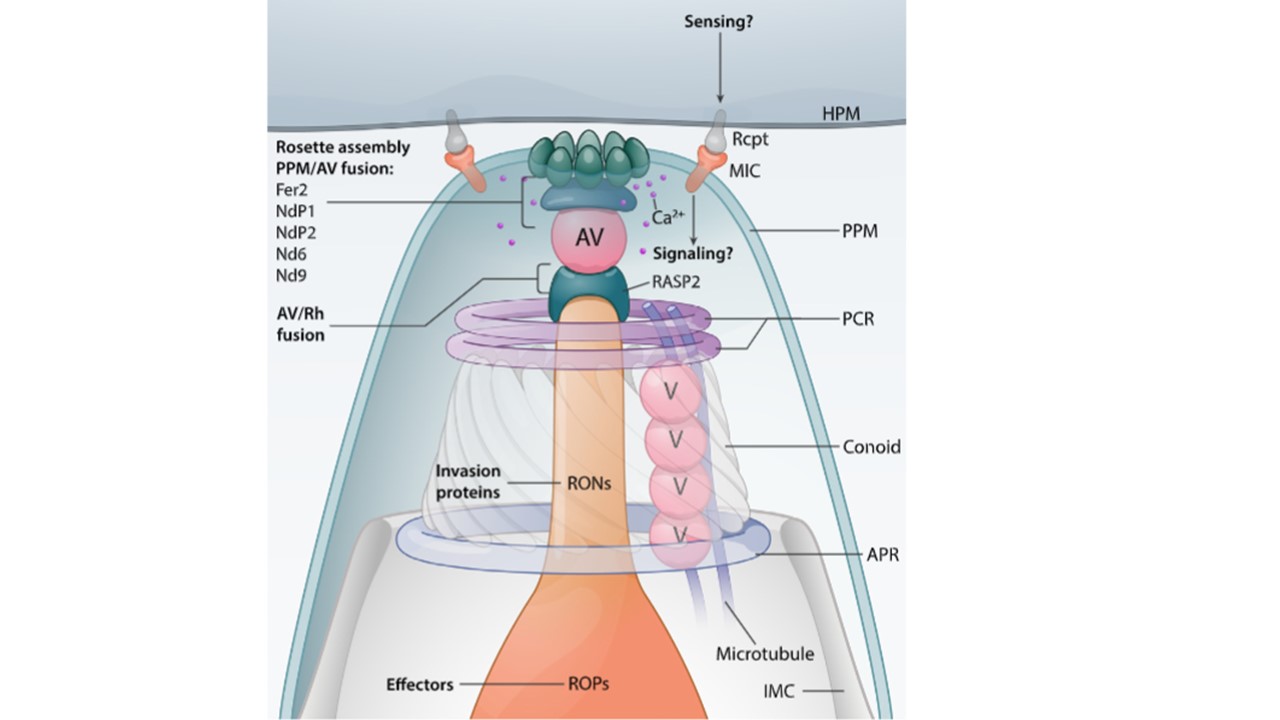
Schematic representation of the apical complex and the fusion events required for rhoptry discharge. Rhoptry exocytosis in T. gondii follows the contact of the parasite's apex with the host cell plasma membrane (HPM), which is mediated by the interaction of microneme proteins (MIC), translocated to the parasite plasma membrane (PPM in light green) upon secretion, with host receptors (Rcpt). Upon such a 'sensing' event, a 'signaling' pathway is likely activated, with a cascade of signals inducing at least two fusion events, one between rhoptry/ies (Rh) and the apical vesicle (AV), and the other between the AV and the PPM, leading to the release of rhoptry neck proteins (RONs) and effectors (ROPs). The Rh/AV fusion might require the rhoptry protein RASP2, which accumulates on the cytoplasmic face of the rhoptry tip, and specifically binds to phosphatidic acid (PA) and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) via its Ca2+-lipid-binding-like (C2) and pleckstrin homology-like (PH) domains, perhaps favoring lipid mixing during the fusion event. The rosette assembly and AV/PPM fusion might instead require a repertoire of proteins, Fer2, NdP1, NdP2, Nd6, and Nd9,which could be part of the connecting density observed by cryo-ET between the apical vesicle and the rosette. This interpretation is based on the accumulation of Nd6 and NdP2 at the apical end of the parasite, and on the fact that they interact with Fer2, NdP1, and Nd9. However, additional functions for these proteins cannot be excluded since they all show a cytoplasmic localization. In addition, Fer2 was shown to accumulate inside the conoid and the cytosolic face of the rhoptry membrane. The RCC1-like domain (RLD) of Nd6 might act as guanine exchange factor towards small GTPases, as previously seen for proteins involved in vesicular membrane fusion. Via its armadillo-like repeats, the Nd9 protein might facilitate protein–protein interactions with other Nd members at the exocytic site in order to assemble the rhoptry secretion apparatus and to stabilize the intramembranous particles (IMPs) of the rosette. The C2domain-containing proteins NdP2 and Fer2 might contribute to the Ca2+-dependent fusion of the AV at the parasite’s membrane. e. PCR, pre-conoidal ring in violet; APR, apical polar ring in light blue; IMC, inner membrane complex in white.
Sparvoli D, Lebrun M. Unraveling the Elusive Rhoptry Exocytic Mechanism of Apicomplexa. Trends Parasitol. 2021 37(7):622-637. PMID: 34045149.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0210600 | cytosolically exposed rhoptry leaflet interacting protein, protein CERLI1 |
| PF3D7_0508500 | nd6 protein, putative |
| PF3D7_0603800 | NdP2 protein, putative |
| PF3D7_1140900 | ndp1 protein, putative |
| PF3D7_1232700 | Nd9 protein |