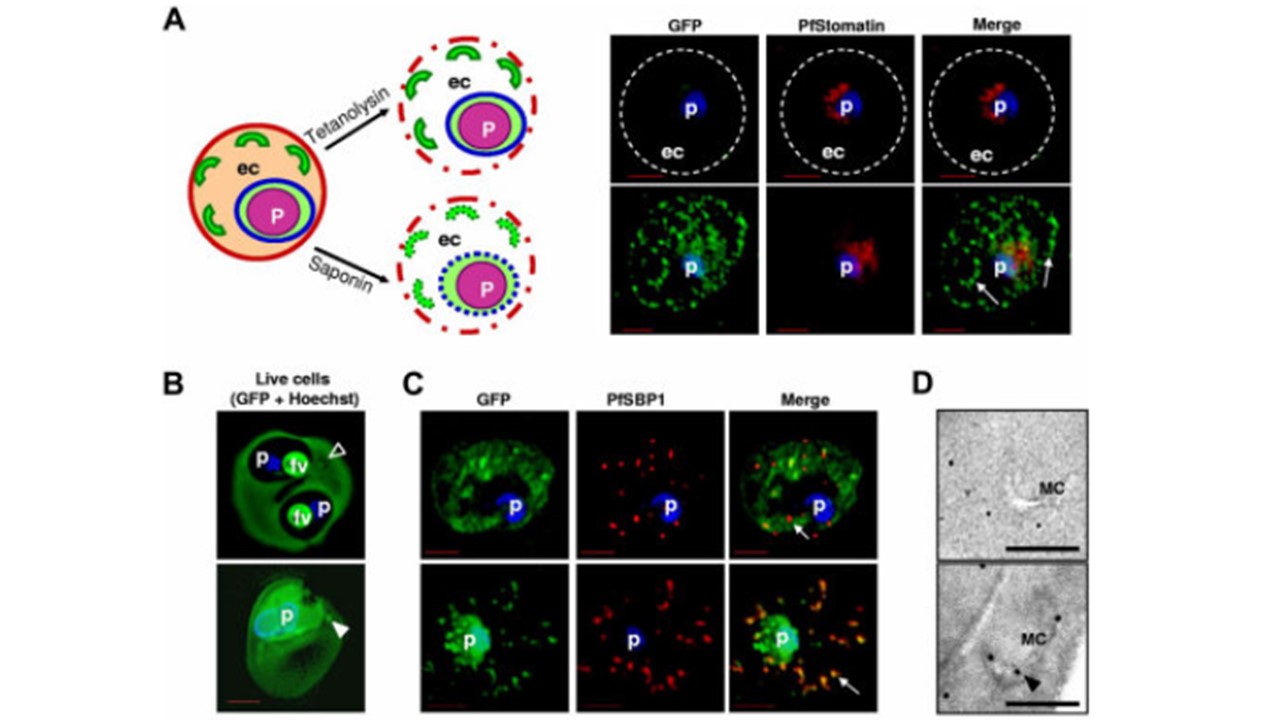
A) Schematic representation of the infected erythrocyte (left) and its permeabilization (dotted lines) after treatment with tetanolysin (top) or saponin (bottom). Panels of fluorescent images show infected erythrocyte expressing HT sol-GFP, permeabilized with tetanolysin (top) or saponin (bottom), and probed with antibodies to GFP (green) and PfStomatin (red). Respective merged images are also shown. Dotted lines indicate erythrocyte periphery. Arrows show intraerythrocytic clefts. (B) 0° projections of an rHT-GFP–loaded erythrocyte ghost infected with 3D7 P falciparum (top) or a mock-loaded erythrocyte ghost infected with transgenic parasite expressing HT-GFP (bottom). Empty arrowhead, cleft structure not labeled with intraerythrocytic rHT-GFP; solid arrowhead, GFP labeled cleft. (C) Cells in panel B fixed, permeabilized, and probed with antibodies to GFP (green) and resident cleft protein PfSBP1 (red). Arrows show clefts. (D) Immunoelectron microscopy of cells in panel B showing distribution of GFP associated with Maurer’s clefts (MC). Bar indicates 500 nm. Bhattacharjee S, van Ooij C, Balu B, Adams JH, Haldar K. Maurer's clefts of Plasmodium falciparum are secretory organelles that concentrate virulence protein reporters for delivery to the host erythrocyte. Blood. 2008 Feb 111(4):2418-26.