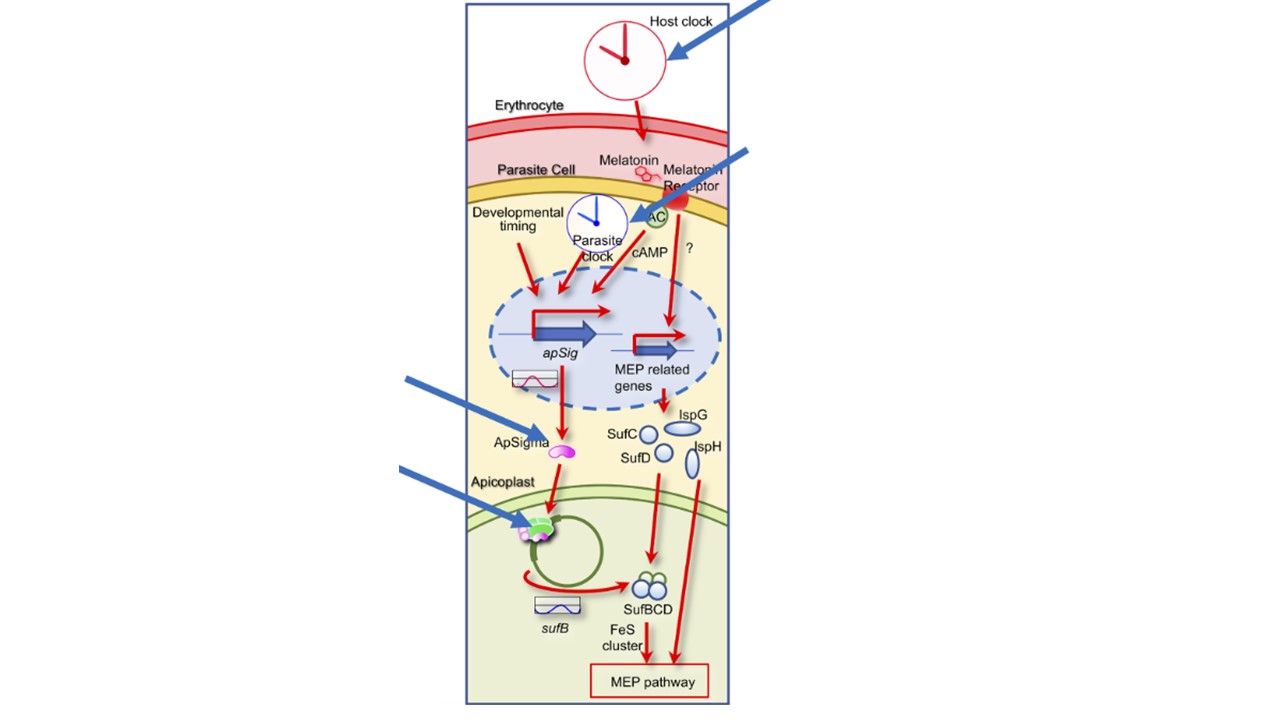
Potential mechanism of regulation of periodic apicoplast gene expression. Apicoplast gene expression has a periodicity. This periodicity is transmitted by the rhythmic expression of rpoA1/2 and apSig by the intrinsic P. falciparum circadian oscillator. In combination, host cues regulate the parasite rhythm. An increase in host melatonin concentration is sensed by melatonin receptors. This signal up- regulates ApSigma expression via cAMP. This increased ApSigma expression may lead to the regulation of periodicity of apicoplast gene expression. The effects of melatonin in this process are influenced by parasite circadian rhythm or developmental stage. Melatonin increases the transcript of sufB encoded by apicoplast DNA and similarly increases the transcripts of sufC, sufD, ispG, and ispH required for the MEP pathway. The activity of the MEP pathway is probably influenced by the host circadian rhythm.
Kobayashi Y, Komatsuya K, Imamura S, Nozaki T, Watanabe YI, Sato S, Dodd AN, Kita K, Tanaka K. Coordination of apicoplast transcription in a malaria parasite by internal and host cues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jul 11;120(28):e2214765120.