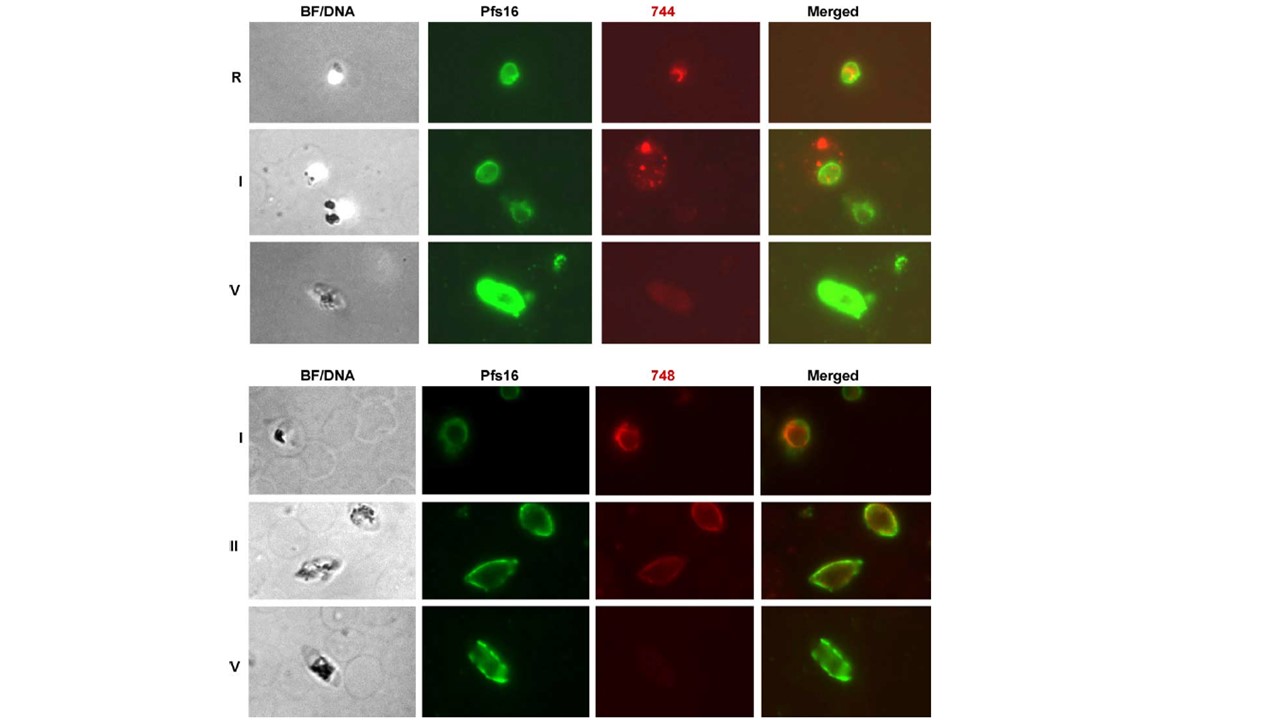
Subcellular localization of Pfg14.744 and Pfg14.748 during gametocytogenesis. Parasites isolated from a non-sychronized gametocyte culture were formaldehyde fixed and permeabilized with 0.1% saponin as described in Section 2, then dual labeled with rabbit anti-Pfs16 and mouse anti-Pfg14.744 (744) or Pfg14.748 (748) antibodies. Representative fields containing early gametocyte committed rings (R) and stage I, II or V gametocytes (I, II, V) are shown. The first panel in each set is a combined bright field and DAPI fluorescence image (BF/DNA) followed by the individual and merged images. As the nascent gametocyte continues to grow Pfg14.744 is detected in the erythrocyte cytoplasm, while Pfg14.748 remains associated with the parasitophorous. This is consistent with the presence of a predicted erythrocyte export motif, RxL/VxE/Q/D (aa 82–86) in Pfg14.744, not Pfg14.748. By stage IV/V of gametocytogenesis neither protein is detectable by IFA, as would be predicted from the steep decline in the mRNA after stage II seen for both genes by Northern.
Eksi S, Haile Y, Furuya T, Ma L, Su X, Williamson KC. Identification of a subtelomeric gene family expressed during the asexual-sexual stage transition in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2005 Sep;143(1):90-9. PubMed
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_1477300 | Plasmodium exported protein (PHIST), unknown function |
| PF3D7_1477700 | Plasmodium exported protein (PHISTa), unknown function |