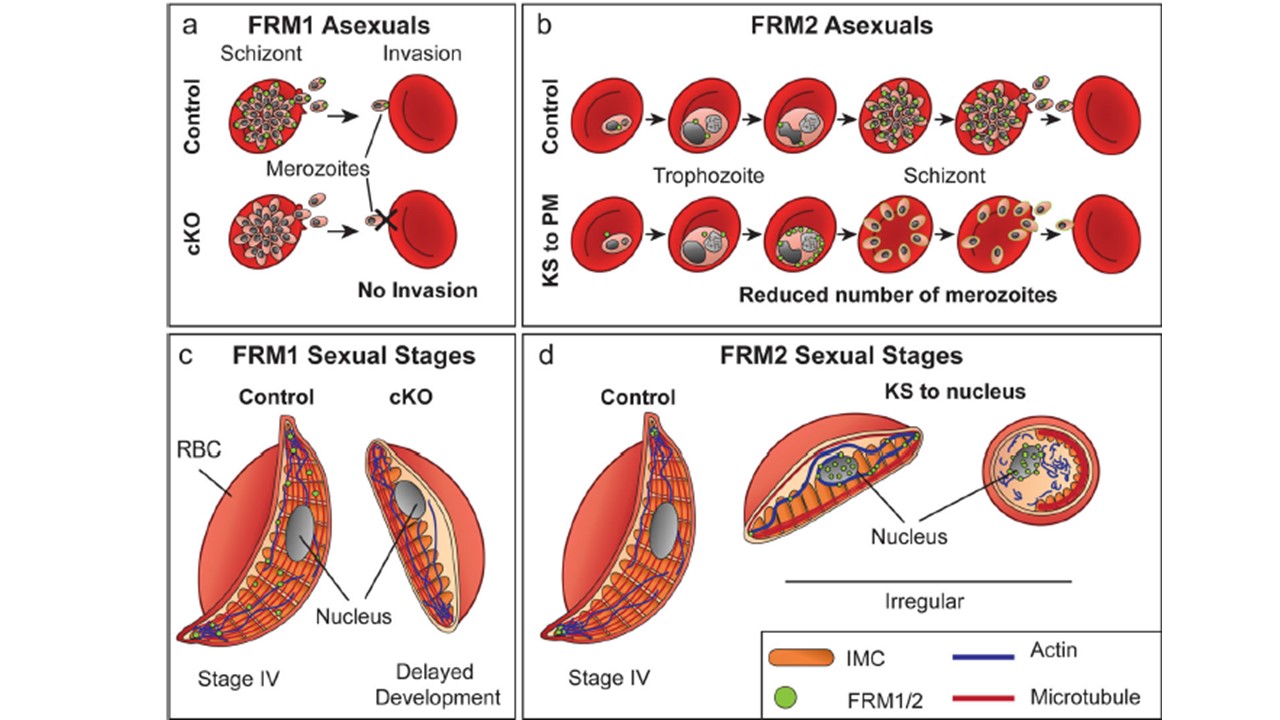
Schematic representation of the functions of formin proteins across blood-stage development. a Asexual stage parasites express FRM1 late in asexual development where it locates at the apical end of the merozoites (green circles). Following conditional knockout (cKO) of FRM1, merozoites are unable to attach and invade RBCs. b FRM2 locates adjacent to the parasite nucleus (green circles), from early trophozoite stage through to merozoites within the schizont. Knock sideways (KS) of the FRM2 protein to the parasite plasma membrane (PM), leads to a reduction in merozoite numbers. c In gametocytes, FRM1 is distributed throughout the cytoplasm (green circles). Conditional knockout (cKO) of FRM1 in gametocytes leads to delayed development. d FRM2 locates at the tips of stage IV gametocytes (green circles) intertwined with the microtubule (red) and actin cytoskeletons (blue). Knock sideways (KS) of the FRM2 to the nucleus leads to a collapse of both the actin and microtubule networks and cells with irregular and round morphologies.
Collier S, Pietsch E, Dans M, Ling D, Tavella TA, Lopaticki S, Marapana DS, Shibu MA, Andrew D, Tiash S, McMillan PJ, Gilson P, Tilley L, Dixon MWA. Plasmodium falciparum formins are essential for invasion and sexual stage development. Commun Biol. 2023 6(1):861.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_1219000 | formin 2 |