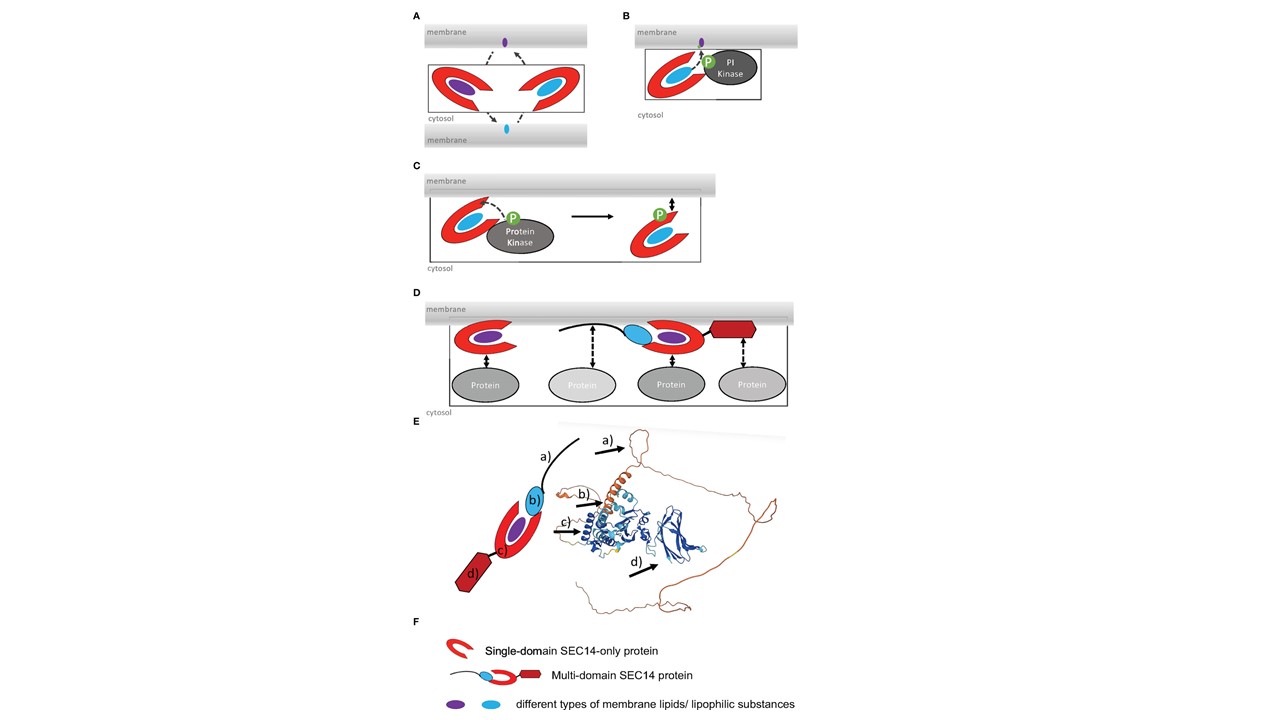
Functions and regulation modes of SEC14L-PITPs (phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins. (A), SEC14 protein-mediated lipid transfer and heterotypic exchange of lipids between two membranes. (B), Lipid presentation model, interaction of SEC14 protein with PI kinase and phosphorylation of lipid during transfer (de Campos and Schaaf, 2017). (C), Regulation of membrane binding by phosphorylation of SEC14 domain by a protein kinase. (D), Increase in the number of potential protein-protein interactions of multi-domain versus single-domain SEC14L-PITPs. (E), Alphafold model of the multi-domain SEC14 protein PATL2 (At1g22530). The arrows point to a) intrinsically disordered N-terminal region; b) CTN domain; c) SEC14 domain with lipid-binding site, gate and anchor helices; d) GOLD domain. Alphafold was used, as described (Jumper et al. 2021; Varadi et al. 2021). (F), Symbols used in (A–D). Montag K, Ivanov R, Bauer P. Role of SEC14-like phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITPs) in membrane identity and dynamics. Front Plant Sci. 2023 14:1181031.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0626400 | CRAL/TRIO /Sec14 domain containing protein |
| PF3D7_0629900 | cral/trio domain-containing protein, putative |
| PF3D7_0920700 | cral/trio domain-containing protein, putative |
| PF3D7_1127600 | CRAL/TRIO domain-containing protein, putative |