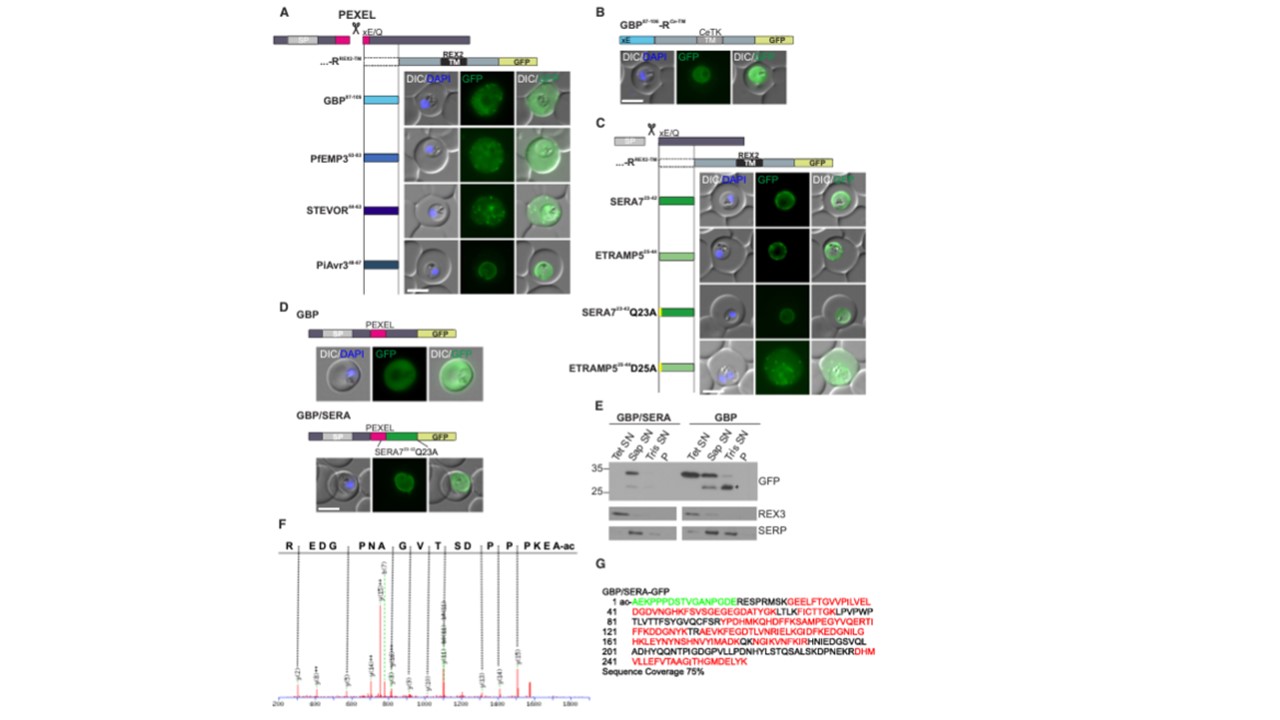
Mature PEXEL N Termini Promote Export of RREX2-TM (A–C) Images of live P. falciparum parasites expressing RREX2-TM fused with the mature N termini of PEXEL proteins (A), GBP87–106-RCe-TM (B), or RREX2-TM fused with the mature N termini of none-xported secretory proteins (C). The position of the appended region in the original protein is shown above each panel. (D) Images of live P. falciparum parasites expressing truncated GBP fused to GFP (GBP, top) or GBP-GFP with the mature N terminus of SERA7Q23A after the PEXEL (GBP/SERA, bottom). (E) Western blot analysis using anti-GFP shows bands with the appropriate size for PEXEL cleavage and confirms that GBP/SERA is in the PV and GBP exported to the host cell. SN, supernatants of: Tet, tetanolysin content of host-cell cytosol); Sap, saponin(PV content);Tris, hypotonic lysis (soluble content in the parasite); and P, pellet (final pellet). REX3, soluble parasite protein in the host cell; SERP, soluble PV marker. Asterisk, degradation product. (F) MS-MS fragmentation spectrum of one species of the most N-terminal detected peptide of GBP/SERA after trypsin digestion. The x axis shows the mass (m/z); the y axis shows the intensity of the y and b ions. (G) Peptides (red; N-terminal peptide in green) from GBP/SERA-GFP detected by MS. ac, acetylation. Size bars represent 5 mm. Image panels are as in Figure 1B. PEXEL and signal-peptide cleavage sites are indicated by scissors; the PEXEL is in magenta, point mutations are in yellow, mature PEXEL N termini are in different shades of blue, and mature N termini of non-exported proteins are in green. Grüring C, Heiber A, Kruse F, Flemming S, Franci G, Colombo SF, Fasana E, Schoeler H, Borgese N, Stunnenberg HG, Przyborski JM, Gilberger TW, Spielmann T. Uncovering common principles in protein export of malaria parasites. Cell Host Microbe. 2012 12(5):717-29.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0930200 | leucine-rich repeat protein |
| PF3D7_0936000 | ring-exported protein 2 |