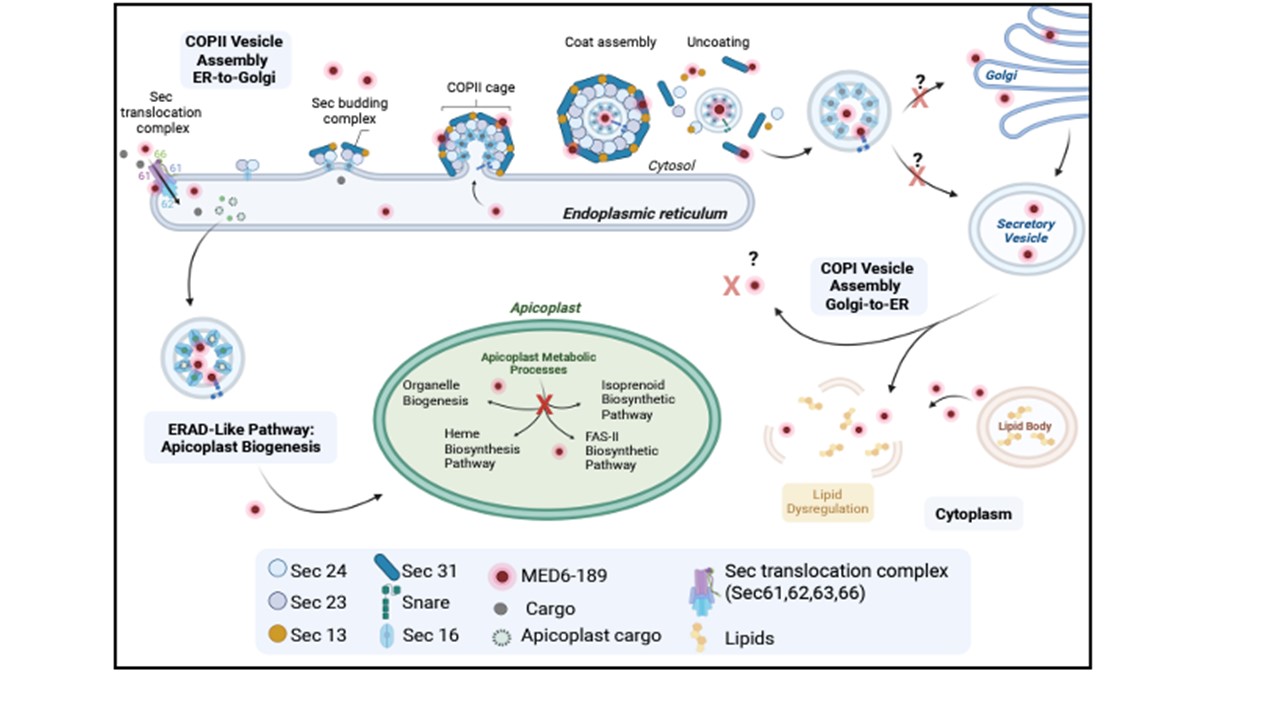
In P. falciparum-infected erythrocytes, compounds are imported into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via the Sec translocation complex (SEC61,62,63,66), where they interact with components of the ER transport machinery. The compounds translocated into the apicoplast where they directly interact with proteins involved in crucial apicoplast function, ultimately disrupting this vital organelle. Chahine Z, Abel S, Hollin T, Chung JH, Barnes GL, Daub ME, Renard I, Choi JY, Pratap V, Pal A, Alba-Argomaniz M, Banks C, Kirkwood J, Saraf A, Camino I, Castaneda P, Cuevas MC, De Mercado-Arnanz J, Fernandez-Alvaro E, Garcia-Perez A, Ibarz N, Viera-Morilla S, Prudhomme J, Joyner CJ, Bei AK, Florens L, Ben Mamoun C, Vanderwal CD, Le Roch KG. A Potent Kalihinol Analogue Disrupts Apicoplast Function and Vesicular Trafficking in P. falciparum Malaria. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023. PMID: 38045341
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0204200 | Translocation protein Sec66 |
| PF3D7_0210000 | secretory complex protein 61 gamma subunit |
| PF3D7_0214100 | protein transport protein SEC31 |
| PF3D7_1116400 | guanine nucleotide-exchange factor SEC12 |
| PF3D7_1361100 | protein transport protein Sec24A |