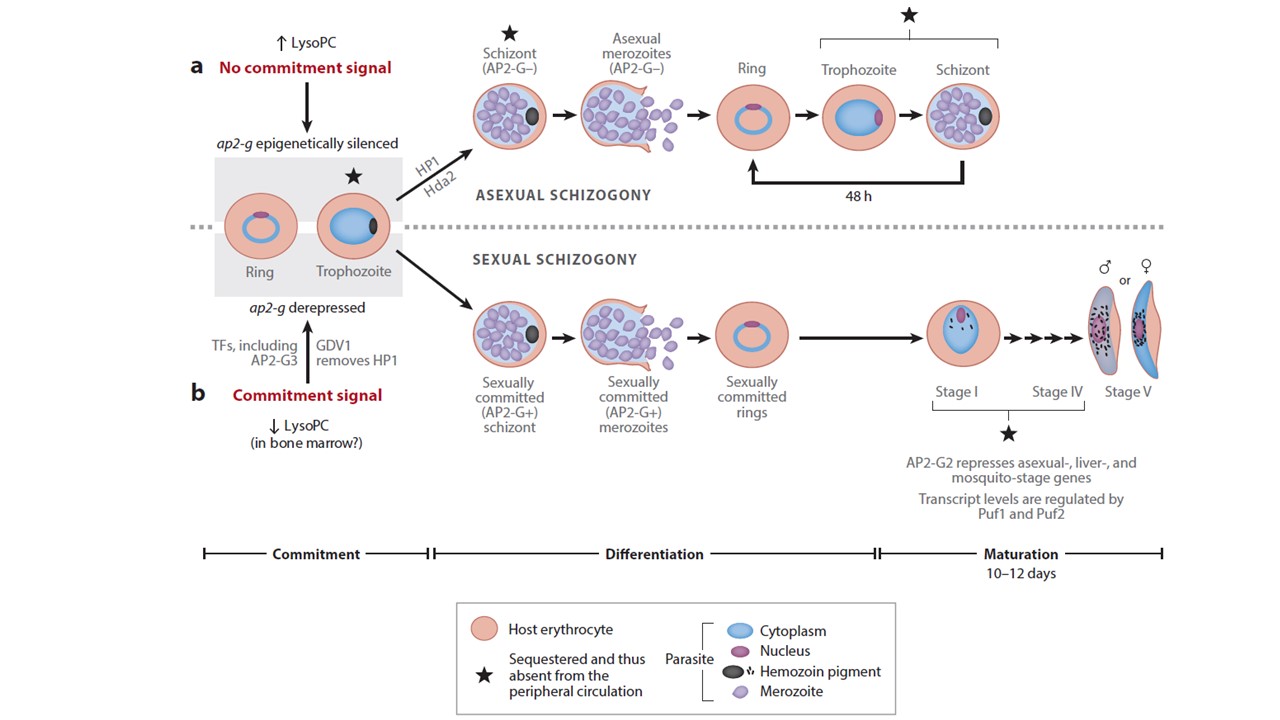
Model for the regulation of commitment and gametocytogenesis. In the presence of lysophosphatidylcholine (LysoPC), the ap2-g locus is epigenetically silenced through the effects of HP1 and Hda2, and cells continue to develop asexually. In the presence of lower levels of LysoPC, parasites are more likely to commit to gametocytogenesis. This process involves the removal of HP1 from the ap2-g locus (likely by GDV1), and transcription of ap2-g (likely by AP2-G3). Downstream of AP2-G, other epigenetic and transcriptional regulators are expressed, thus continuing the gametocyte transcriptional program while AP2-G2 simultaneously represses asexual-, liver-, and mosquito-stage genes. RNA-binding proteins such as Puf1 and Puf2 are important in modulating transcript levels.
Josling GA, Williamson KC, Llinás M. Regulation of Sexual Commitment and Gametocytogenesis in Malaria Parasites. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2018