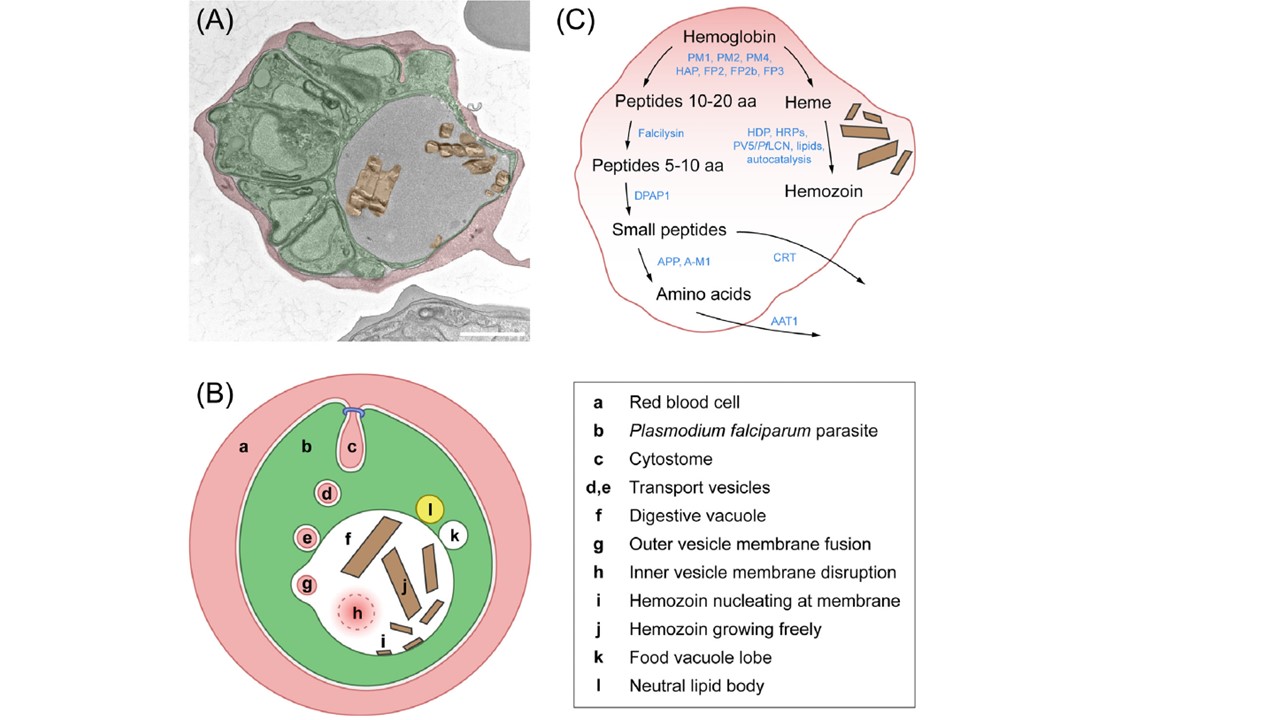
Endocytic trafficking and proteolytic degradation of hemoglobin by malaria parasites. (A) Pseudocolorized transmission electron microscopy (EM) image of a Plasmodium falciparum schizont-infected red blood cell (RBC). Image courtesy of Matthew R.G. Russell (Francis Crick Institute, King’s College London, London, UK). Red, erythrocyte cytoplasm; green, parasite; brown, hemozoin crystals inside the digestive vacuole. Bar, 1 μm. (B) Schematic representation of a P. falciparum-infected RBC. Structures and events involved in host cell cytosol uptake and hemoglobin-to-hemozoin transition are marked with lower-case letters and are listed in the legend to the right. (C) Catalytic steps in the processing of hemoglobin and the biomineralization of heme. Blue color denotes molecules with
confirmed or suggested roles in catalysis. Abbreviations: aa, amino acids; AAT1, amino acid transporter 1; A-M1, M1-family alanyl aminopeptidase; APP, aminopeptidase P; CRT, chloroquine resistance transporter; DPAP1, dipeptidyl aminopeptidase 1; FP2, 2b, 3, falcipains 2, 2b, 3; HAP, histo-aspartic protease; HDP, heme detoxification protein; Matz JM. Plasmodium's bottomless pit: properties and functions of the malaria parasite's digestive vacuole. Trends Parasitol. 2022 38(7):525-543.