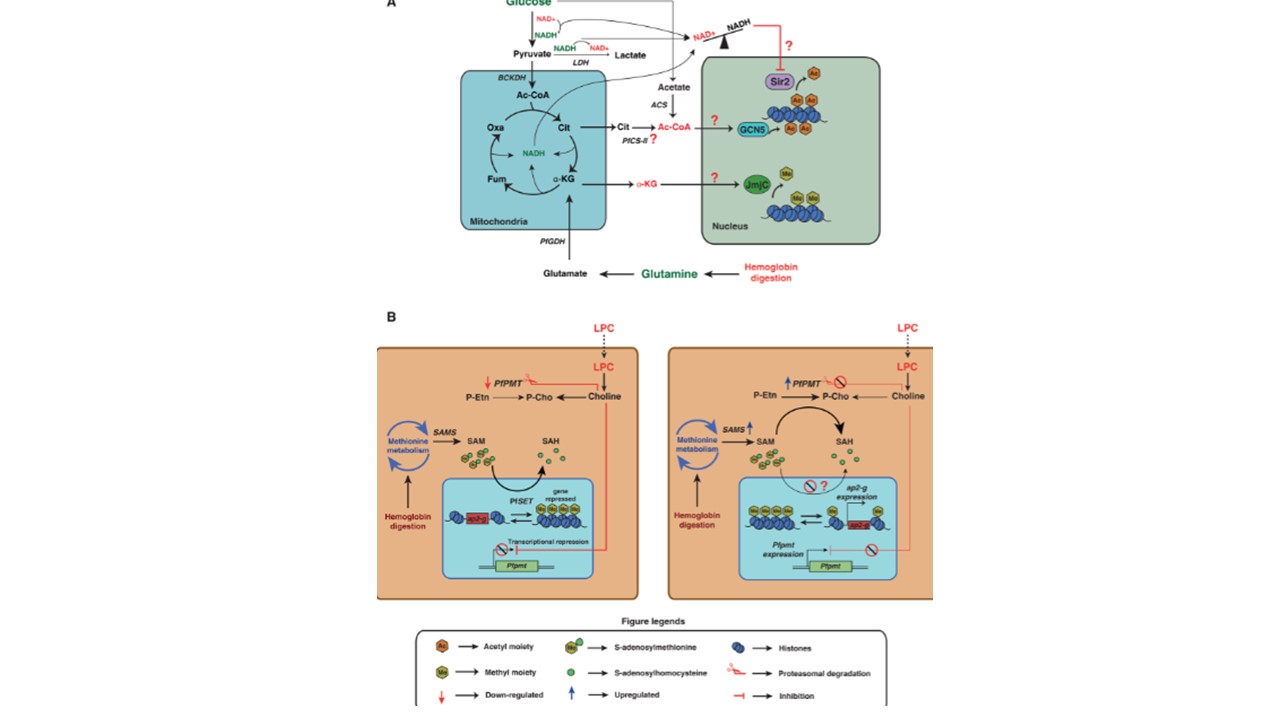
A) NADH/NAD+ levels are influenced by the rate of glycolysis, fermentation and the TCA cycle, which could affect the activity of NAD+-dependent histone deacetylases (sirtuins). Acetyl-CoA generated through carbon metabolism is used by PfGCN5 for acetylation of histones, which regulate gene expression. Glutamine is converted to α-ketoglutarate, which is a co-factor for histone demethylase enzymes. B) Host LysoPC is converted into choline by the parasite. Under LysoPC depletion, conditions, PfPMT and enzymes involved in SAM generation were found to be overexpressed. Increased utilization of SAM by the PfPMT enzyme for the synthesis of phosphocholine may affect nuclear pools of SAM leading to hypomethylation of histones, allowing expression of genes such as pfap2-g. Abbreviations: Ac-CoA, acetyl-CoA; Oxa, oxalic acid; Cit, citrate; αKG, α-ketoglutarate; Fum, Fumarate, ACS, Acetyl-CoA synthetase; BCKDH, branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase; CS-II, Citrate synthease II; Sir2, Sirtuin histone deacetylase; JmjC, JmjC domain containing histone demethylase; SAM, S-Adenosylmethionine; P-Etn, phosphoethanolamine; P-Cho, phosphocholine; GDH, Glutamate dehydrogenase; LDH, Lactate dehydrogenase; PfSET, SET domain-containing protein methyltransferase. Kumar M, Skillman K, Duraisingh MT. Linking nutrient sensing and gene expression in Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage parasites. Mol Microbiol. 2021 May;115(5):891-900. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14652. Epub 2020 Dec 13. PMID: 33236377