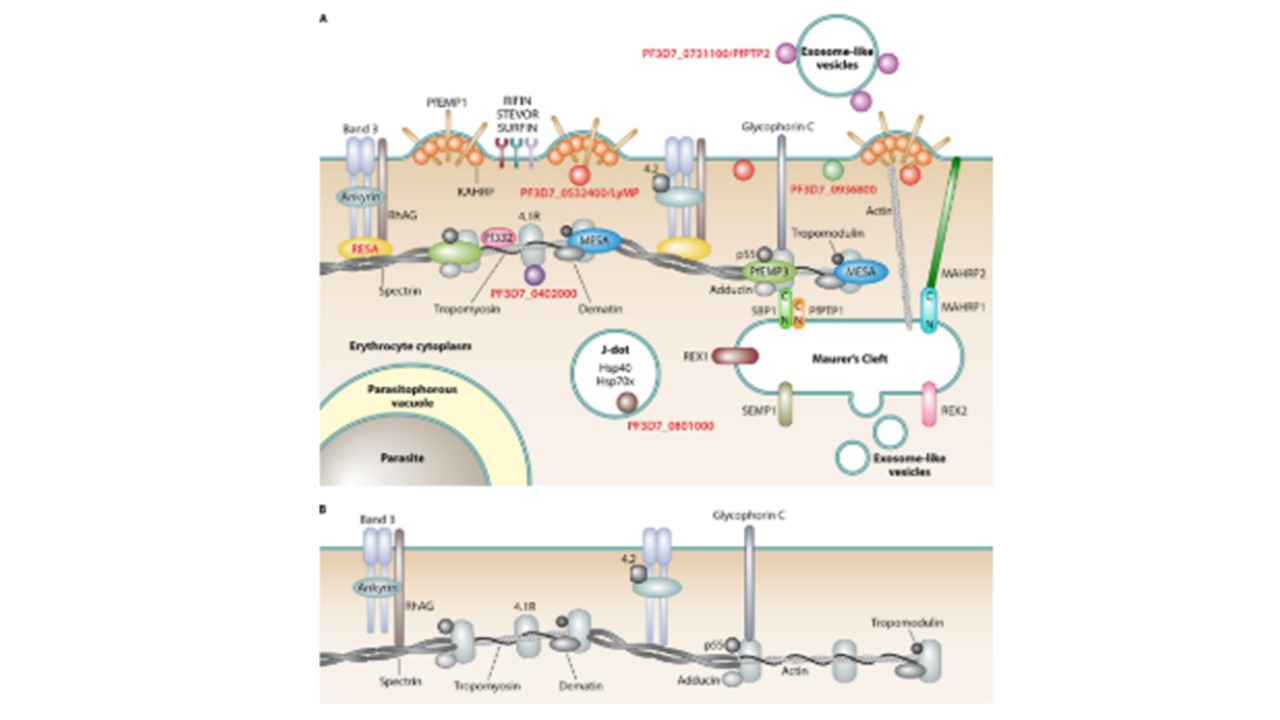
. (A) Remodeled iRBC. During the asexual blood stage of P. falciparum, human erythrocytes are subject to extensive remodeling. All erythrocyte proteins are shown in. Parasite structures, compartments, and organelles are labeled in boldface type. PHIST proteins are labeled in red boldface type, and all parasite proteins are represented by colored shapes. References for PHIST proteins are indicated in the text. Knobs are parasite-derived protrusions in the host cell membrane, with KAHRP being a prominent protein of these structures. Maurer's clefts (reviewed in reference 151) are parasite-derived membranous structures in the iRBC cytoplasm involved in protein trafficking and are connected with knobs via actin filaments. Maurer's cleft-associated histidine-rich protein 1 (MAHRP1) is a Maurer's cleft-resident protein that potentially interacts with MAHRP2, the tether protein anchoring Maurer's clefts to the iRBC membrane. REX1, REX2, SEMP1, SBP1, and PfPTP1 are other exported parasite proteins that localize to Maurer's clefts, with the latter two being located in a high-molecular-weight complex (159) and SBP1 interacting with the erythrocyte cytoskeleton proteins spectrin and band 4.1R . J dots are mobile, dot-like structures in iRBCs. PfPTP2 is associated with exosomes, which are parasite-derived vesicles that are involved in cell-cell communication between iRBCs. RhAG, rhesus-associated antigen. (B) Cytoskeleton of an uninfected red blood cell. Warncke JD, Vakonakis I, Beck HP. Plasmodium Helical Interspersed Subtelomeric (PHIST) Proteins, at the Center of Host Cell Remodeling. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27582258