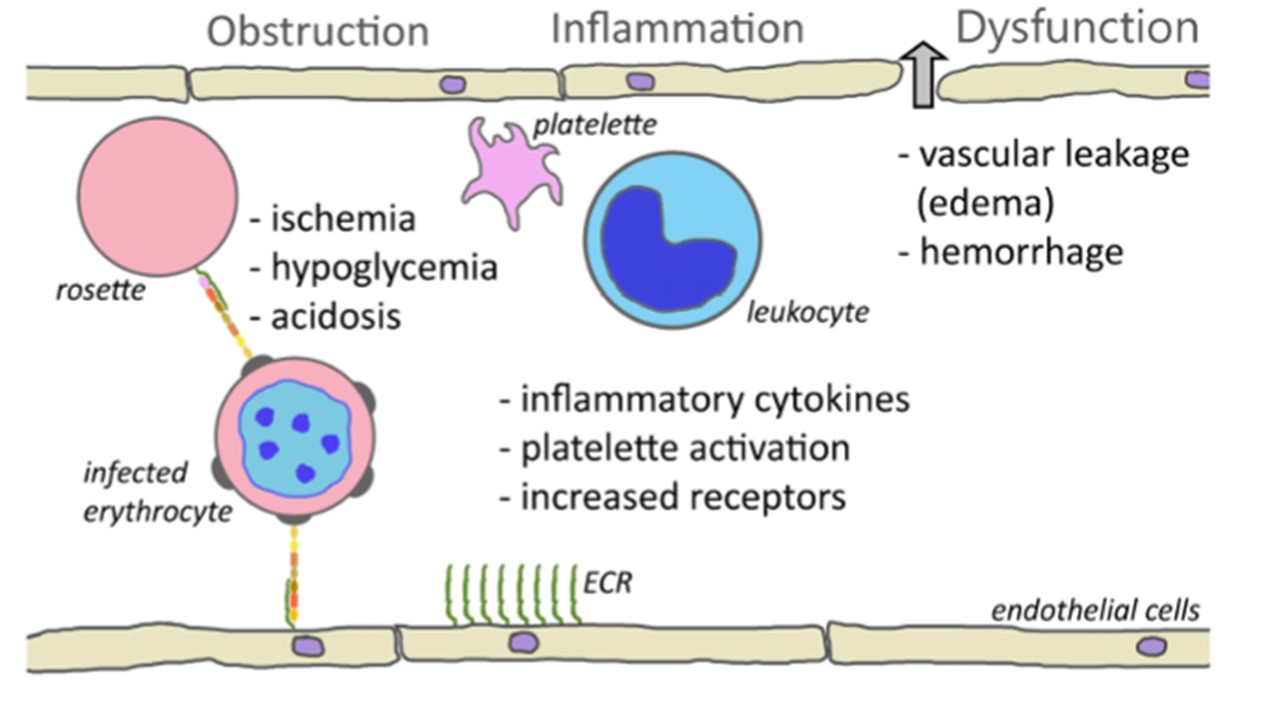
Cytoadherence mediated pathogenesis.
One consequence of cytoadherence is the obstruction of capillaries. Rosetting and platelet mediated clumping may augment this obstruction. Obstruction of blood vessels results in reduced blood flow and ischemia. This decreased perfusion combined with parasite metabolism may contribute to hypoglycemia and acidosis. Cytoadherence also inflames the endothelium and attracts leukocytes and activates platelets. This inflammation and increased levels of inflammatory cytokines cause a loosening of the tight junctions between endothelial cells and results in leakage of fluid into the tissues or hemorrhaging (block arrow). Inflammation also increases the expression of endothelial cell receptors (ECRs) and may augment cytoadherence. also inflames the endothelium and attracts leukocytes and activates platelets. This inflammation and increased levels of inflammatory cytokines cause a loosening of the tight junctions between endothelial cells and results in leakage of fluid into the tissues or hemorrhaging (block arrow). Inflammation also increases the expression of endothelial cell receptors (ECRs) and may augment cytoadherence. Wiser MF. Knobs, Adhesion, and Severe Falciparum Malaria. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023