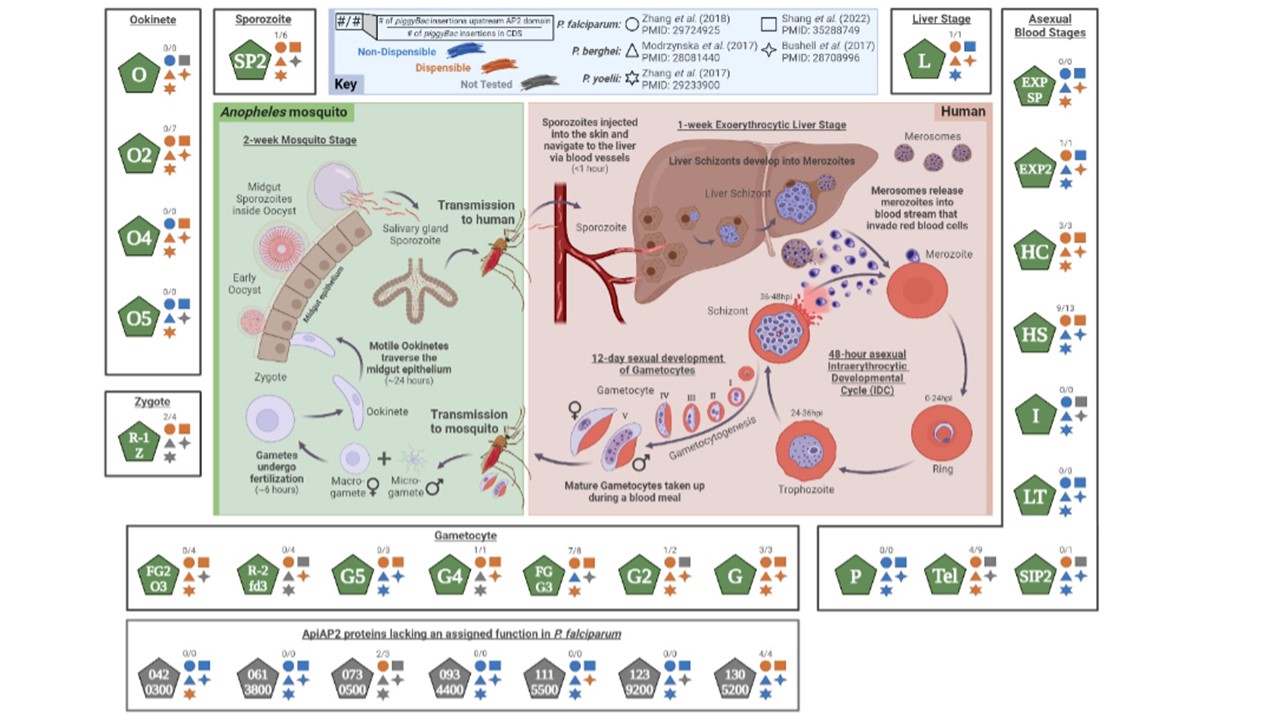
ApiAP2 proteins function as transcription regulators at all developmental stages of the malaria parasite life cycle. The largest family of P. falciparum sequence-specific transcription factors (TFs) is the 30-membered Apicomplexan APETALA2 (ApiAP2) family of DNA-binding proteins (represented as pentagons). As their name implies, many ApiAP2 proteins are highly conserved between apicomplexan species. ApiAP2 proteins are also ubiquitous to all Plasmodium species and have been identified as critical transcriptional regulators of all developmental processes of the parasite lifecycle. ApiAP2 proteins that regulate developmental transitions are denoted at the stage at which they have been most comprehensively characterized or at the stage at which parasites carrying a deletion of the gene encoding the protein are no longer able to develop further. The smaller shapes depict apiap2 gene mutagenesis results from large scale reverse genetic screens in P. falciparum (circle [PMID: 29724925] and square [PMID: 35288749]), P. berghei (triangle [PMID: 28081440] and four-point star [PMID: 28708996]), and P. yoelii (six-point star [PMID: 29233900]). A blue symbol depicts that the apiap2 gene was not dispensable in the respective genetic screen. An orange symbol depicts dispensable genes. Gray symbols indicate that the ApiAP2 protein was not tested in that particular genetic screen. For example, the gene encoding AP2-I has not been deleted in any species and is therefore marked as non-dispensable (blue), although PfAP2-I has been demonstrated to regulate a number of genes associated with invasion and rhoptry formation [PMID: 28618269]. On the other hand, the gene encoding AP2-O was successfully deleted in P. berghei and P. yoelii (but not P. falciparum), resulting in a failure to develop ookinetes because this gene is dispensable in the asexual blood stages of rodent malaria parasites. Please note that this categorization of ApiAP2 proteins does not exclude the likely possibility that several ApiAP2 proteins may have roles in multiple stages of the parasite life cycle. The number of piggyBac insertions upstream of the AP2 domain and the number of piggyBac insertions in the CDS for each ApiAP2 protein is depicted as #/# (from [PMID: 29724925]). This figure was originally published in the review by Singhal et al. 2024 [PMID: 39419713].
Abbreviation: hpi, hours post invasion.
Compiled by Manuel Linas