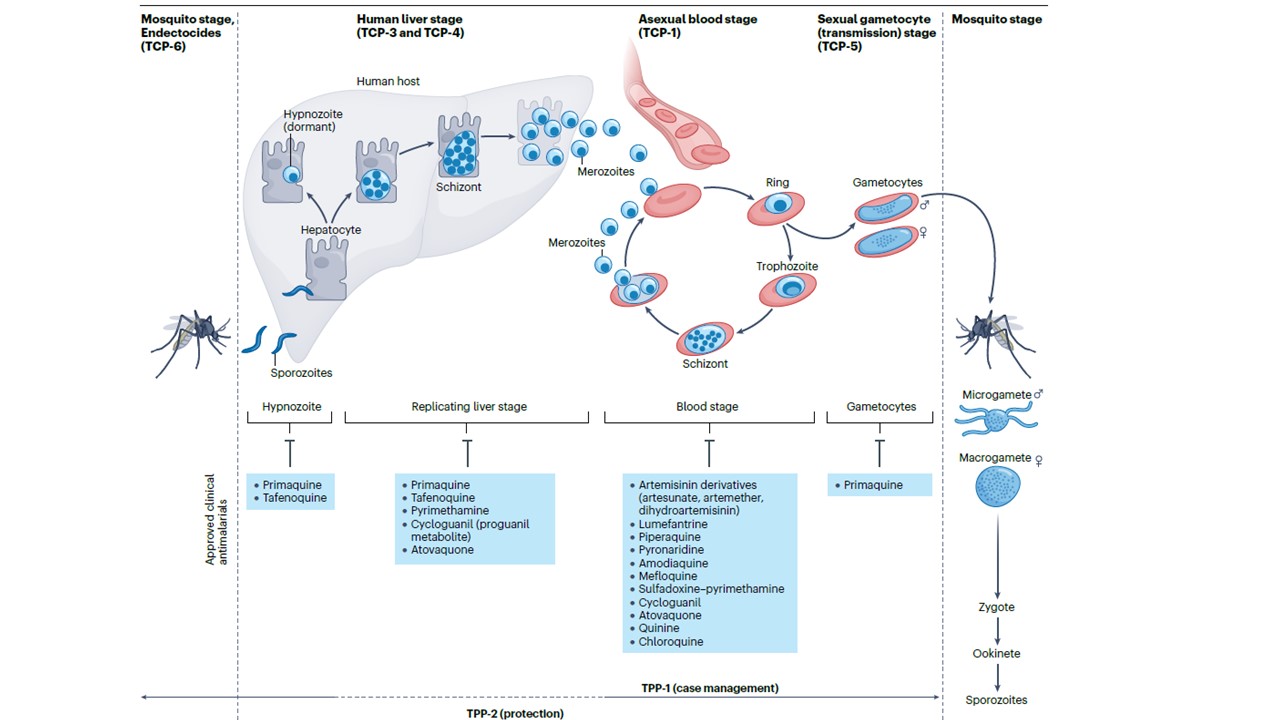
During its blood meal on a human host, the female Anopheles species mosquito delivers sporozoites that enter the skin and subsequently target liver cells (hepatocytes). Within the liver, the parasite matures into schizonts (or dormant hypnozoites for Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale), followed by bursting merozoites that invade erythrocytes (the asexual blood stage). The parasite forms a ring in each erythrocyte that grows into a trophozoite with an acidic digestive vacuole that digests haemoglobin to liberate peptides and amino acids required for protein synthesis. These parasites mature into multinucleated schizonts, from which thousands of merozoites rupture, allowing for rapid replication as they reinvade new red blood cells. Small percentages of merozoites differentiate into male and female gametocytes to initiate the sexual transmission stage, where parasites are ingested by a female mosquito during its blood meal to continue the cycle. Antimalarial drugs that act on the asexual blood stage are categorized as target candidate profile 1 (TCP-1), whereas molecules active against liver-stage hypnozoites (P. vivax) or hepatic schizonts are in categories TCP-3 and TCP-4, respectively. Drugs that block transmission to the mosquito by inhibiting gametocytes are TCP-5 compounds, and those that block transmission by targeting the insect vector are TCP-6 (endectocides). Two or more compounds are combined into clinical therapies with target product profile 1 (TPP-1) and TPP-2 (ref. 240). TPP-1 focuses on drugs for chemotherapeutic treatment of
acute uncomplicated malaria in children or adults, using compounds with TCP-1; if possible, TCP-3, TCP-4 and TCP-5 compounds are added to reduce relapse, provide post-treatment prophylaxis and block transmission. TPP-2 focuses on prevention, in high-transmission areas or during epidemics, and gives protection via TCP-1 and, ideally, TCP-4 for prophylaxis and TCP-5 to clear gametocytaemia in asymptomatic individuals. Antimalarials approved for clinical use are listed for each TCP category.
Siqueira-Neto JL, Wicht KJ, Chibale K, Burrows JN, Fidock DA, Winzeler EA. Antimalarial drug discovery: progress and approaches. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 37652975.