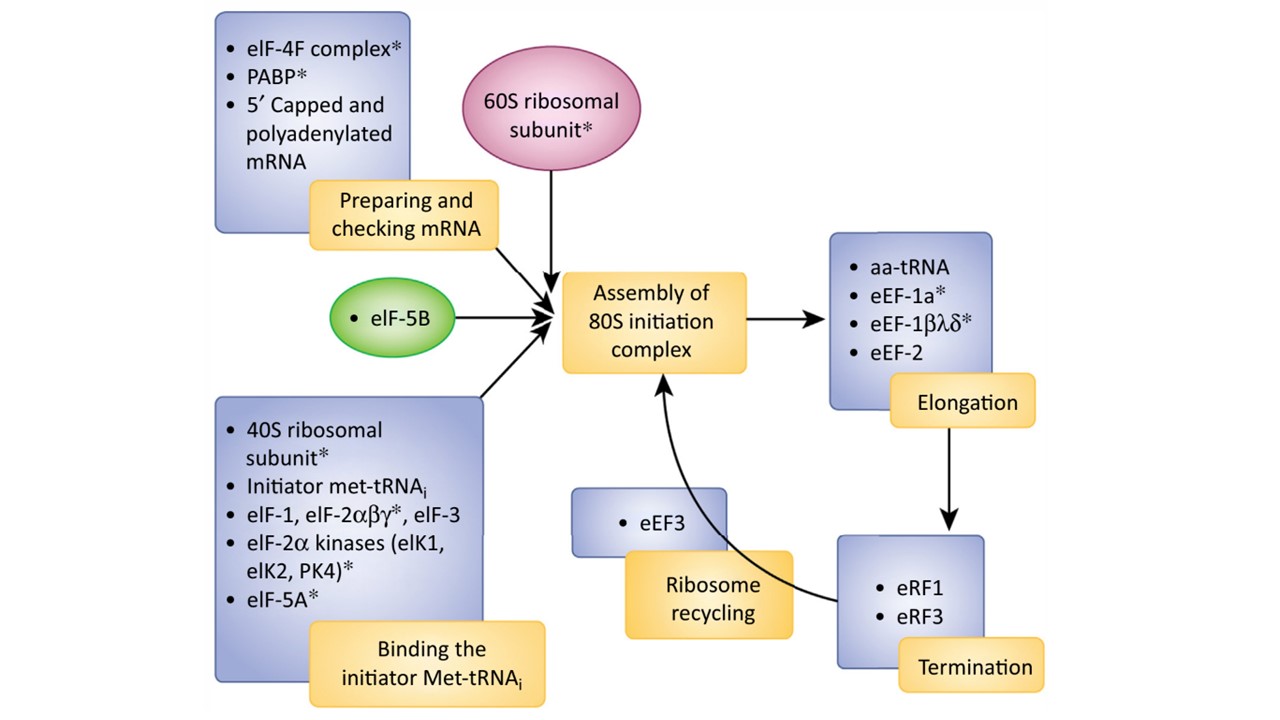
Steps in the assembly of a translation-competent initiation complex followed by elongation, peptide release, and recycling of ribosomes are shown. Experimentally identified factors and ribosome components are marked by *. Among apicomplexan parasites, components of the cytosolic translation apparatus have been studied mainly in P. falciparum. Cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions of blood stage 80S ribosomes from the parasite cytosol indicate conserved features of the core region but also identify differences such as the presence of 18S rRNA expansion segments with a possible role in translation regulation, and the absence of receptor for activated C kinase (RACK1) from its binding site near the mRNA exit channel. Nuclear rDNA genes are differentially expressed in parasite life-cycle stages (A-type in the liver and blood, O-type in the ookinete, and S-type in the sporozoite), implying the presence of stage-specific functions of Plasmodium cytosolic ribosomes. A translation-competent complex operates through stepwise interactions of individual factors and factor assemblies and most of these are identified in Plasmodium spp.. The heterotrimeric eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF)4F complex (consisting of eIF4A helicase, scaffold eIF4G, and eIF4E) that associates with 50 m7 GpppN cap and the poly(A)-binding protein (PABP) to form a closed-loop mRNA–protein structure has been identified in P. falciparum. Translation initiates with the binding of initiator Met-tRNA that is brought to the mRNA-containing 40S ribosome by eIF2. Components of eIF2 (/, b, and g) are annotated in P. falciparum and three eIF2/ kinases (eIK1, eIK2, and PK4) with roles in stress response and stage-specific translation repression are known. The hypusine-containing eIF5A is likely to enhance the activity of eIF2 and stimulate initiation together with eIF1. An eIF5B would be required for association of 60S and 40S subunits accompanied by release of other eIFs. The translation elongation complex (eEF1/ that brings aa-tRNA to the A-site and its GTP recycling factor eEF1b, g, and d) has been isolated from P. falciparum blood stages. Although the elongation factor eEF2 has not been characterized, its identification as an inhibitor target suggests functionality. Peptide release factors eRF1 and eRF3 are also recognized on the P. falciparum genome as is the ribosome recycling factor eEF3. Cytosolic translation in the parasite is regulated at different stages in its life cycle by cis elements in mRNA, RNA-binding proteins, RNA-processing enzymes, and phosphorylation.
Habib S, Vaishya S, Gupta K. Translation in Organelles of Apicomplexan Parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2016 32(12):939-952. PMID: 27527393.
>