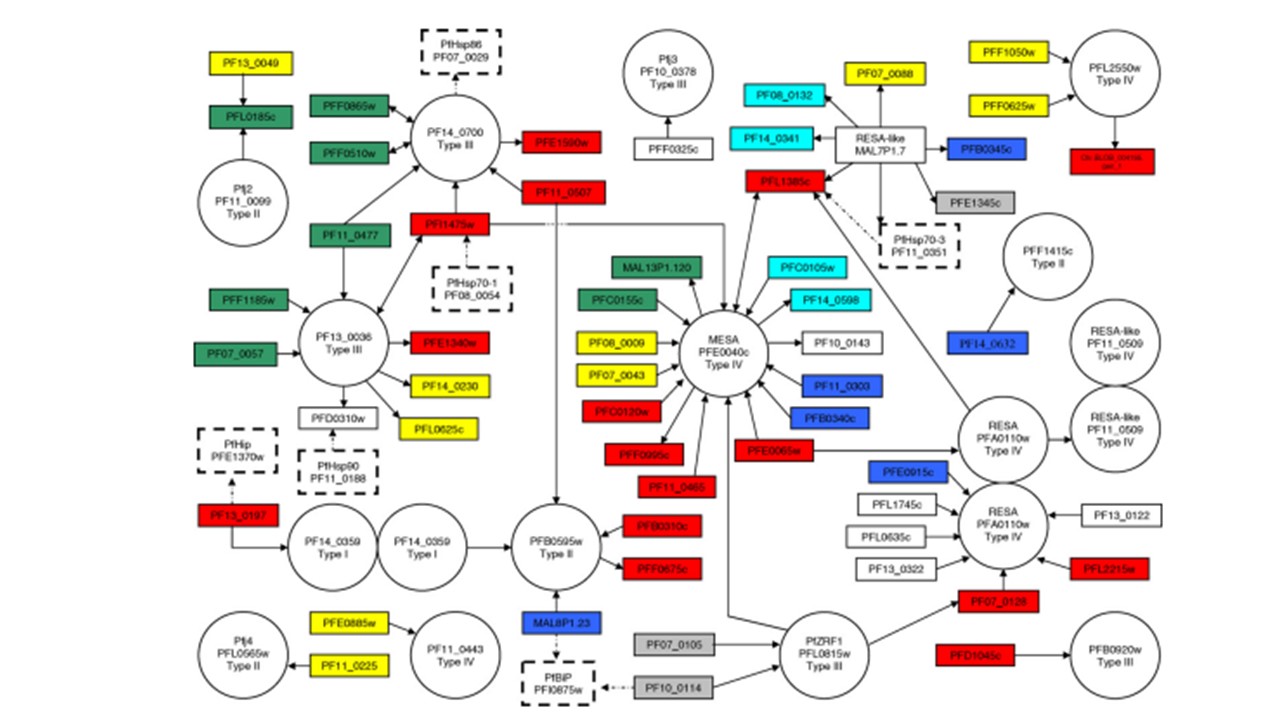
The predicted protein-protein interactions involving members of the P. falciparum Hsp40 protein family were extracted from a yeast two-hybrid analysis. Hsp40 proteins are indicated in circles with a common name if designated, their locus accession number, and a classification according to Hsp40 types (I–IV). Members of the Hsp70, Hsp90 and Hip protein families of P. falciparum are indicated in dashed boxes. The RESA-like protein MAL7P1.7 is not an Hsp40 protein and hence it is housed in a box. This RESA-like protein was included with its set of interactors because of its similarity to the RESA protein family, and because one of its interactors is PfHsp70-3. Potential protein interactors are indicated by their locus accession number in solid boxes and classified into functional categories as indicated with color: red, cytoskeletal and membrane proteins; blue, the proteasome and proteolytic enzymes; yellow, translational machinery; green, transcriptional machinery; turquoise, enzymes involved in cellular physiology; grey, DNA repair and replication machinery; white, unclassified. The association of prey with bait proteins in the yeast two-hybrid assays is indicated with the directional arrows pointing to the prey for single associations (bait→prey), and a double headed arrow for reciprocal associations. If an Hs40 protein self associates, a double circle is drawn. The abbreviated common names for certain of the P. falciparum (Pf) proteins are defined as follows: Pfj2-4, the Hsp40 proteins described by Watanabe (1997); PfZRF1, a protein similar to the human zuotin-related factor 1; PfBiP,immunoglobulin binding protein or ER Hsp70 homolog; PfHip, Hsp70-interacting protein homolog; PfHsp90, heat shock protein 90 homolog; PfHsp86, heat shock protein 86 homolog. Botha M, Pesce ER, Blatch GL. The Hsp40 proteins of Plasmodium falciparum and other apicomplexa: regulating chaperone power in the parasite and the host. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007 PMID: 17428722.