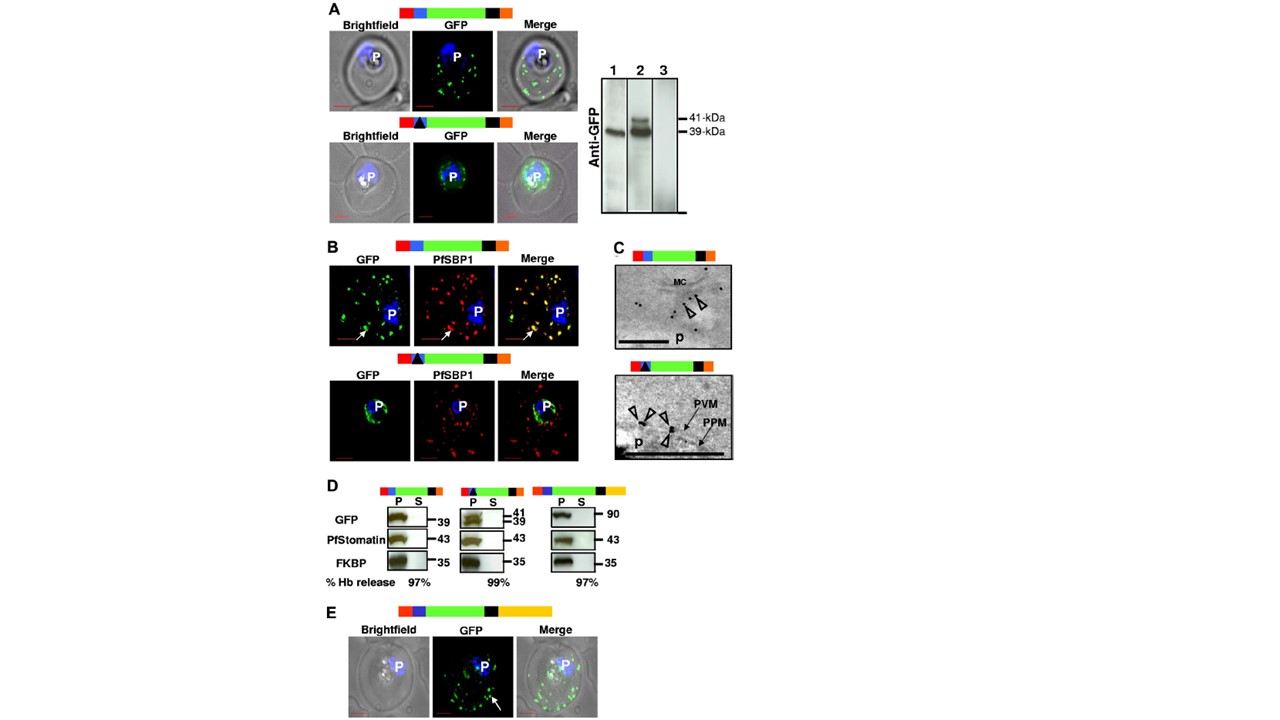
The HT motif targets proteins to Maurer’s clefts without translocation into the erythrocyte cytoplasm. (A) Live infected erythrocytes expressing HT-GFPmembmyc (top) and D-GFPmembmyc (bottom) viewed under bright-field image, GFP fluorescence, and merged optics. Western blot using antibodies to GFP indicating the detection of 39-kDa fusion product for HT-FPmembmyc-expressing cells (lane 1), 39/41-kDa doublet fusion product for D-GFPmembmyc-expressing cells (lane 2), or no signal for untransfected cells (lane 3) is shown at the right. In lane 2, the
41-kDa band is a precursor that in pulse chase experiments can be chased into the 39-kDa band (data not shown). Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate repositioned gel lanes. (B) Indirect immunofluorescence assay showing distribution of GFP (green), associated with HT-GFPmembmyc (top panel) or D-GFPmembmyc (bottom panel) relative to the Maurer’s cleft protein PfSBP1 (red). Parasite nucleus (p) is stained with Hoechst 33342. (C) Localization of HT-GFPmembmyc in Maurer’s clefts (MC, top) and D-GFPmembmyc in parasitophorous vacuolar membrane (PVM, bottom) by immunoelectron microscopy. Empty arrowheads indicate gold particles showing distribution of GFP chimeras. Bar, 500 nm; p, parasite. Micrograph at the bottom has been magnified twice compared with that at the top to distinguish the parasite plasma membrane (PPM) from the PVM. (D) Western blots of tetanolysin-released infected erythrocyte cytoplasm supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions of cells expressing HT-GFPmembmyc (left panel), D-GFPmembmyc (middle panel), and HT-GFPmembC-term (right panel) probed for GFP, PVM marker PfStomatin, and parasite cytoplasmic protein PfFKBP. Hemoglobin (Hb) released (in S) by tetanolysin is expressed as a percentage of the total Hb detected by hypotonic lysis. (E) Live infected erythrocytes expressing HT-GFPmembCterm viewed under bright-field image, GFP fluorescence, and merged optics. Schematic representation for all constructs are indicated above with ER-type signal sequence (red), sequence containing HT signal (blue) or its replacement (solid black triangle) fused to GFP (green), transmembrane region (black), and myc (orange). C-terminal region (derived from PfEMP1) is depicted in yellow. Bhattacharjee S, van Ooij C, Balu B, Adams JH, Haldar K. Maurer's clefts of Plasmodium falciparum are secretory organelles that concentrate virulence protein reporters for delivery to the host erythrocyte. Blood. 2008 111(4):2418-26. PMID: 18057226