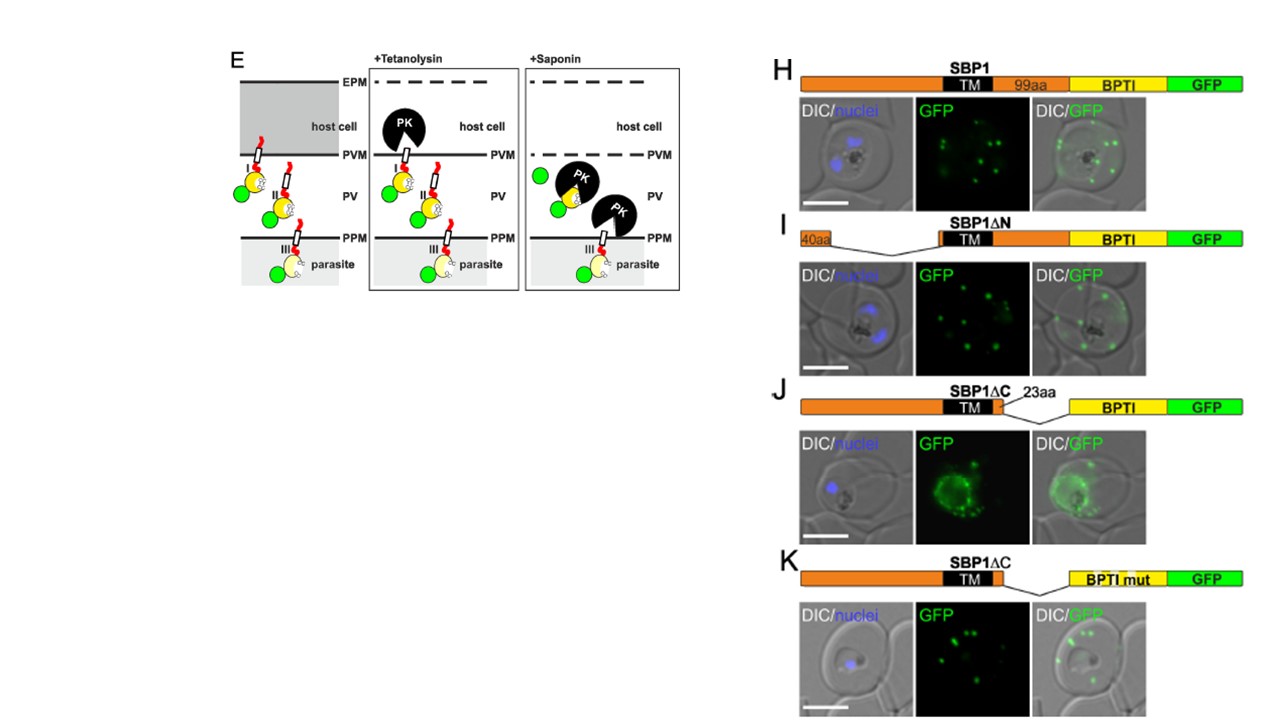
Fusion with the redox sensitive BPTI reveals a second translocation step for TM proteins. (A-D and F-L) Representative images of live P. falciparum parasites expressing the constructs shown schematically above each panel. Hydrophobic regions (SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane domain) are in black, the PEXEL motif in yellow. Numbers refer to amino acids (aa). Red boxes labelled C, additional REX2 C-termini. Interrupted yellow box, mutated BPTI (BPTImut). DIC, differential interference contrast. Size bars: 5 μm. (E) Schematic for the protease K (PK) protection assay. Left, intact infected RBC with 3 possibilities (I, II, III) for the location of the fusion construct: I, protein is integral to PVM; II, protein is freely accessible in the PV; III, protein is integral to PPM. Middle, after permeabilisation of the erythrocyte plasma membrane (EPM) with tetanolysin the N-terminus of the construct will be digested if it is in the PVM (I), but remains intact in situation II and III. Right, after permeabilisation of the PVM with saponin, the constructs will be digested if it is in the PVM (I) or the PV (II) but if in the PPM (III), an N-terminally truncated fragment will be generated. Red, exported protein; white box, TM; yellow, BPTI with double cysteine bonds; green, GFP. Mesén-Ramírez P, Reinsch F, Blancke Soares A, Bergmann B, Ullrich AK, Tenzer S, Spielmann T. Stable Translocation Intermediates Jam Global Protein Export in Plasmodium falciparum Parasites and Link the PTEX Component EXP2 with Translocation Activity. PLoS Pathog. 2016 May 11;12(5):e1005618
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0501300 | skeleton-binding protein 1 |
| PF3D7_0936300 | ring-exported protein 3 |