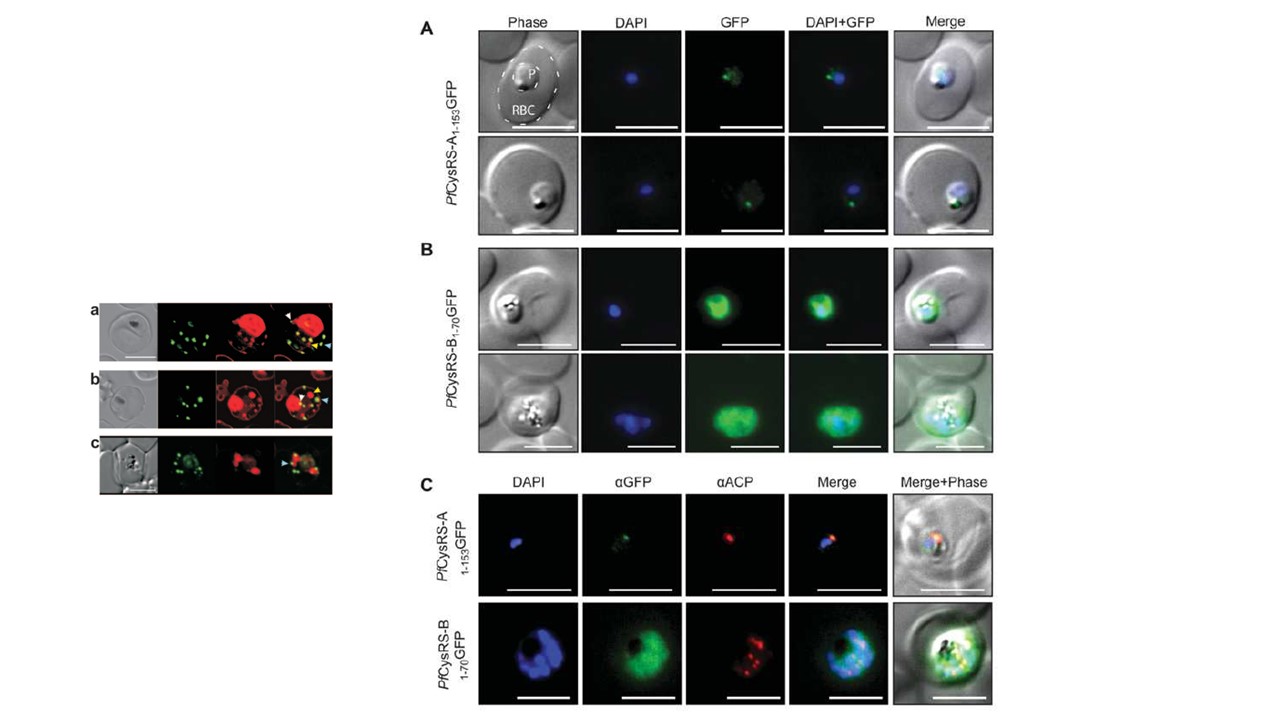
Localization of Pf CysRS isoforms using GFP fusions in transgenic Plasmodium parasites Live-cell epifluorescence microscopy of P. falciparum transfected using pGlux.1 vector for episomal expression of GFP fused to the two Pf CysRS mRNA isoforms: Pf CysRS-A1–153GFP (A) and Pf CysRS-B1–70GFP (B) in live cells. In (A), both parasites are early trophozoite stage, and localization of GFP is to a single punctum, consistent with the size and position of the apicoplast. The red blood cell (RBC) and the parasite (P) are indicated. (B) An early trophozoite (top panels) and late trophozoite (bottom panels) with GFP dispersed throughout the cytosol. (C) Immunofluorescence assays of the parasites indicated, PfCysRS-A1–153GFP (top panels) and PfCysRS-B1–70GFP (bottom panels), using antibodies against GFP and ACP, an apicoplast marker. The PfCysRS-A1–153GFP signal specifically co-localizes with the apicoplast marker, whereas the Pf CysRS-B1–70GFP signal is distributed throughout the cytosol. For (A)–(C), all scale bars indicate 5 μm.
Small picture: Dual labeling of MAHRP11-249-GFP transfectants with BODIPY-ceramide. (a to c) The images represent (from left to right) a DIC image, GFP fluorescence, BODIPY-ceramide fluorescence, and an overlay of the GFP (green) and BODIPY-ceramide (red) images. The parasite membranes are intensely labeled with the lipid probe. Some extensions of the PV membrane are dotted with foci of MAHRP1-GFP (white arrows). Some of the BODIPY-labeled structures (probably TVN extensions and buds) are not labeled with GFP (yellow arrows), while others (presumably Maurer’s clefts) are labeled with GFP (blue arrows). The fluorescence images in panel c correspond to an average projection generated from a series of optical slices. Bar, 5 μm.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_1370300 | membrane associated histidine-rich protein |