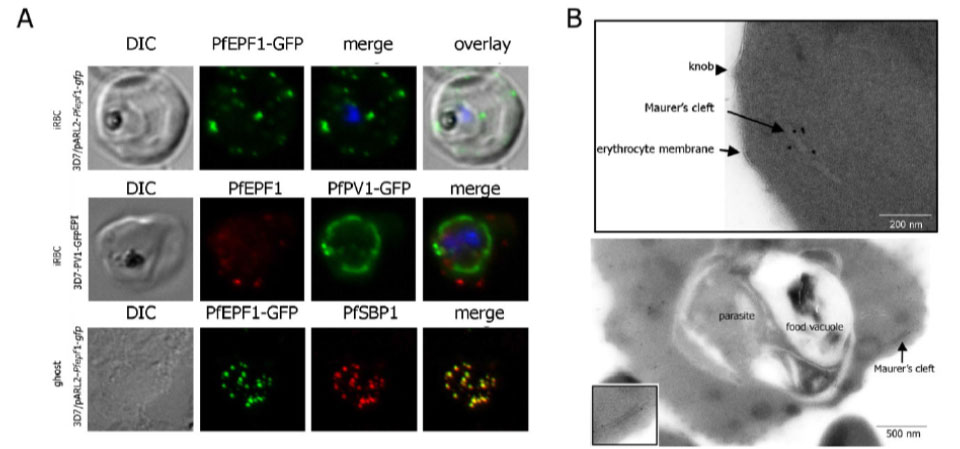
Localization and topology of the PfEPF1 proteins. A. Fluorescent patterns of iRBCs infected by 3D7/pARL2-Pfepf1-gfp (live imaging) and 3D7/PV1-GFPEPI (GFP fluorescence, in green, and immunodetection using anti-PfEPF1 antibodies, in red) and of resealed ghosts from 3D7/pARL2-Pfepf1-gfp iRBCs (GFP fluorescence, in green, and immunodetection using anti-SBP1, in red, antibodies). RBCs and ghost preparations were incubated with DAPI for nucleus labelling. B. Immunoelectron microscopy using anti-GFP antibodies. The inset shows higher magnification of a labelled Maurer’s cleft. Fluorescent dots in the iRBC cytoplasm; some at the erythrocyte periphery are suggestive of Maurer’s clefts while others are observed at the periphery of the parasitophorous vacuole. The Maurer’s cleft localization of the protein was confirmed by its colocalization with PfSBP1.
Mbengue A, Audiger N, Vialla E, Dubremetz JF, Braun-Breton C. Novel Plasmodium falciparum Maurer's clefts protein families implicated in the release of infectious merozoites. Mol Microbiol. 2013 88(2):425-42
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0501300 | skeleton-binding protein 1 |
| PF3D7_1129100 | parasitophorous vacuolar protein 1 |