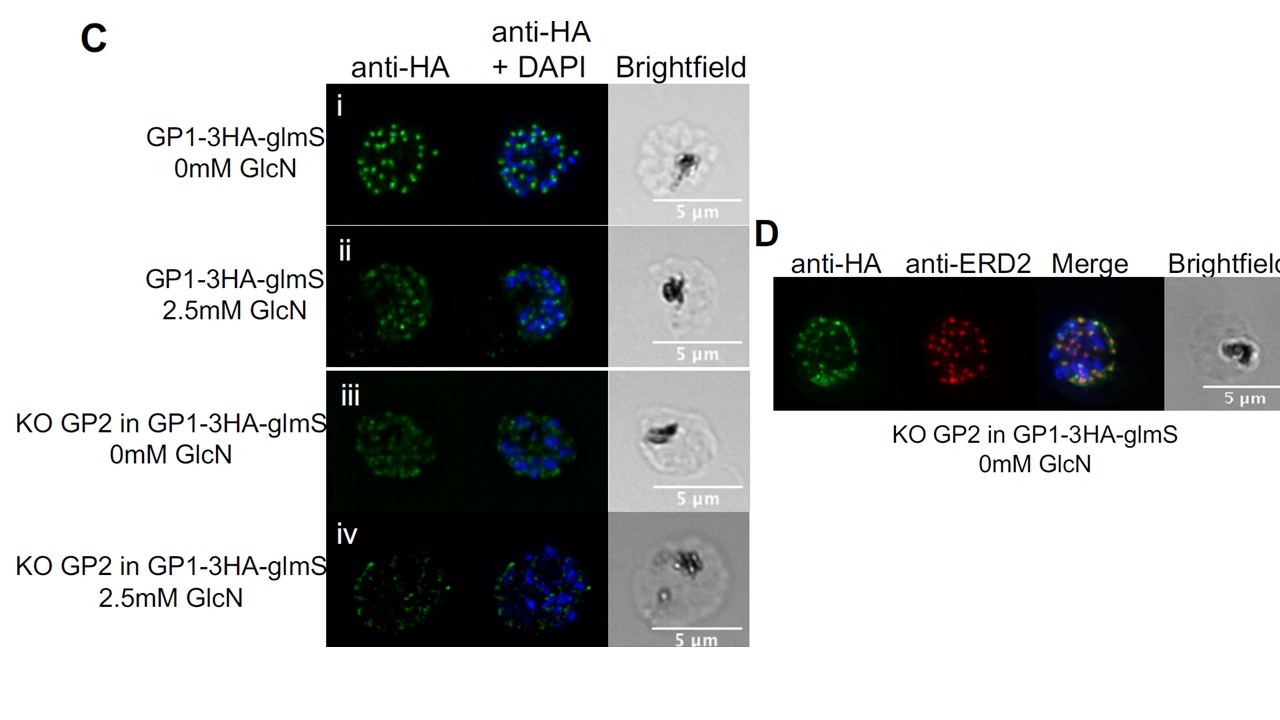
Knocking down GP1 and knocking out GP2 in the same parasite line results in reduced asexual parasite survival. (C) IFA showing the reduction of the GP1 signal after knockdown induction (ii) compared to the untreated parasites (i) in the GP1-3HA-glmS line. (iii) Knocking out GP2 causes the mislocalisation of a portion of GP1-3HA. (iv) Knocking out GP2 and knocking down GP1 leads to an almost complete loss of the GP1 signal by IFA. Scale bar represent 5 µm. (D) IFA showing that the residual punctate pattern of GP1-3HA in the KOGP2 line still overlaps with ERD2. Note that the green channel was overexposed to capture more HA signal and allow the colocalisation analysis.
Hallée S, Theriault C, Gagnon D, Kehrer J, Frischknecht F, Mair GR, Richard D.Identification of a Golgi apparatus protein complex important for the asexual erythrocytic cycle of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Cell Microbiol.2018 Mar 26:e12843.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_1320000 | rhoptry protein 2, putative golgi protein 1 |
| PF3D7_1353600 | ER lumen protein retaining receptor |