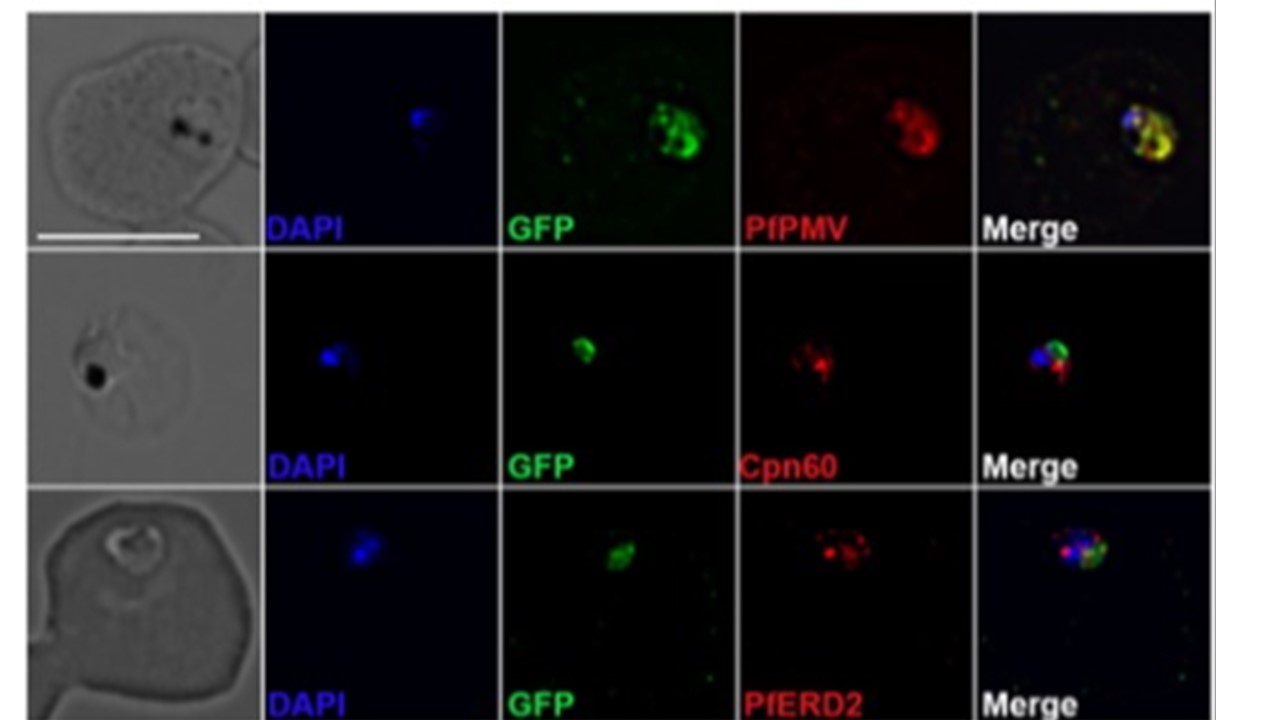
Putative PfGRP170 apicoplast transit peptide localises to the ER and conditional inhibition of PfGRP170 does not affect trafficking of apicoplast proteins. (b) PfGRP170's putative apicoplast transit peptide was fused to GFP and transfected into 3D7 parasites. Parasites were fixed with acetone and stained with DAPI, anti‐GFP (to label the PfGRP170 putative transit peptide) and either anti‐PfPMV (ER), anti‐PfERD2 (Golgi), or anti‐Cpn60 (apicoplast) to determine subcellular localisation. The images were taken with Delta Vision II, deconvolved, and are displayed as a maximum intensity projection. The scale bar is 5 μm. (c) Synchronised ring stage PfGRP170 parasites were incubated for 24 hr with and without TMP. Following the incubation, the parasites were fixed with paraformaldehyde and stained with DAPI, anti‐GFP (PfGRP170), and anti‐Cpn60 (apicoplast). Images were taken as a Z‐stack using super resolution microscopy and SIM processing was performed on the Z‐stacks. Images are displayed as a maximum intensity projection. The scale bar is 2 μm. Kudyba HM, Cobb DW, Fierro MA, Florentin A, Ljolje D, Singh B, Lucchi NW, Muralidharan V. The endoplasmic reticulum chaperone PfGRP170 is essential for asexual development and is linked to stress response in malaria parasites. Cell Microbiol. 2019 21(9):e13042. PMID: 31087747;
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_1232100 | 60 kDa chaperonin |
| PF3D7_1344200 | PfHsp70-y |
| PF3D7_1353600 | ER lumen protein retaining receptor |