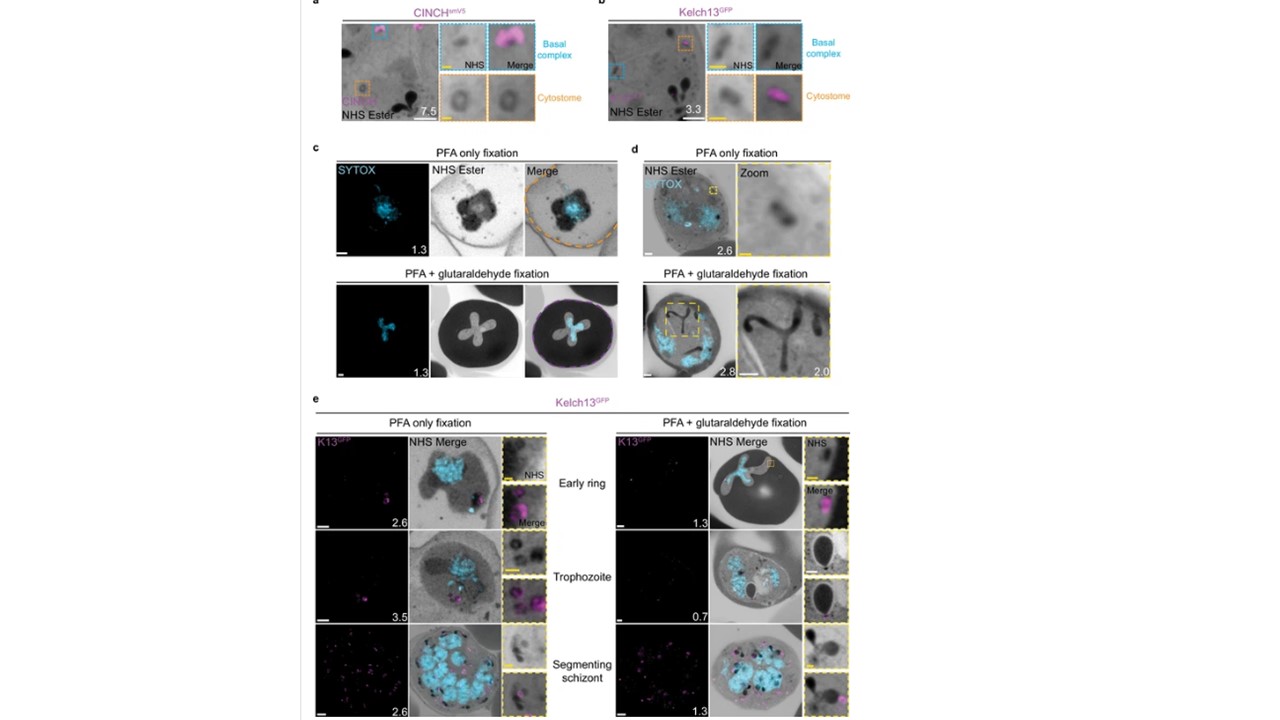
Cytostomes are observable by ultrastructural expansion microscopy (U-ExM) throughout the asexual blood stage of the lifecycle. (a) Parasites expressing an smV5-tagged copy of the basal complex marker CINCH, prepared by U-ExM, and stained with anti-V5, show N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester-dense rings that are negative for this basal complex marker. (b) Parasites prepared by U-ExM where the cytostome marker Kelch13 was conjugated to GFP (K13-GFP) and stained with anti-GFP. Image shows co-localization between K13-GFP and the putative cytostome. NHS ester-dense ring. (c) Comparison between paraformaldehyde (PFA)-only and PFA-glutaraldehyde fixed U-ExM parasites, showing lysed (PFA only, orange) and intact (PFA-glutaraldehyde, magenta) red blood cell (RBC) membranes. (d) In PFA-only fixed parasites, only the cytostomal collar is preserved, while both the collar and bulb are preserved upon PFA-glutaraldehyde fixation. (e) K13-GFP parasites were either fixed in PFA only or PFA-glutaraldehyde, prepared by U-ExM, stained with NHS ester (grayscale), SYTOX (cyan), and anti-GFP (cytostome) (magenta) antibodies and imaged using Airyscan microscopy across the asexual blood stage. Zoomed regions show cytostomes. Images are maximum-intensity projections, number on image = Z-axis thickness of projection in µm. White scale bars = 2 µm, yellow scale bars = 500 nm. Xie SC, Ralph SA, Tilley L. K13, the Cytostome, and Artemisinin Resistance. Trends Parasitol. 2020 36(6):533-544. PMID: 32359872.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0407800 | coordinator of nascent cell detachment CINCH |