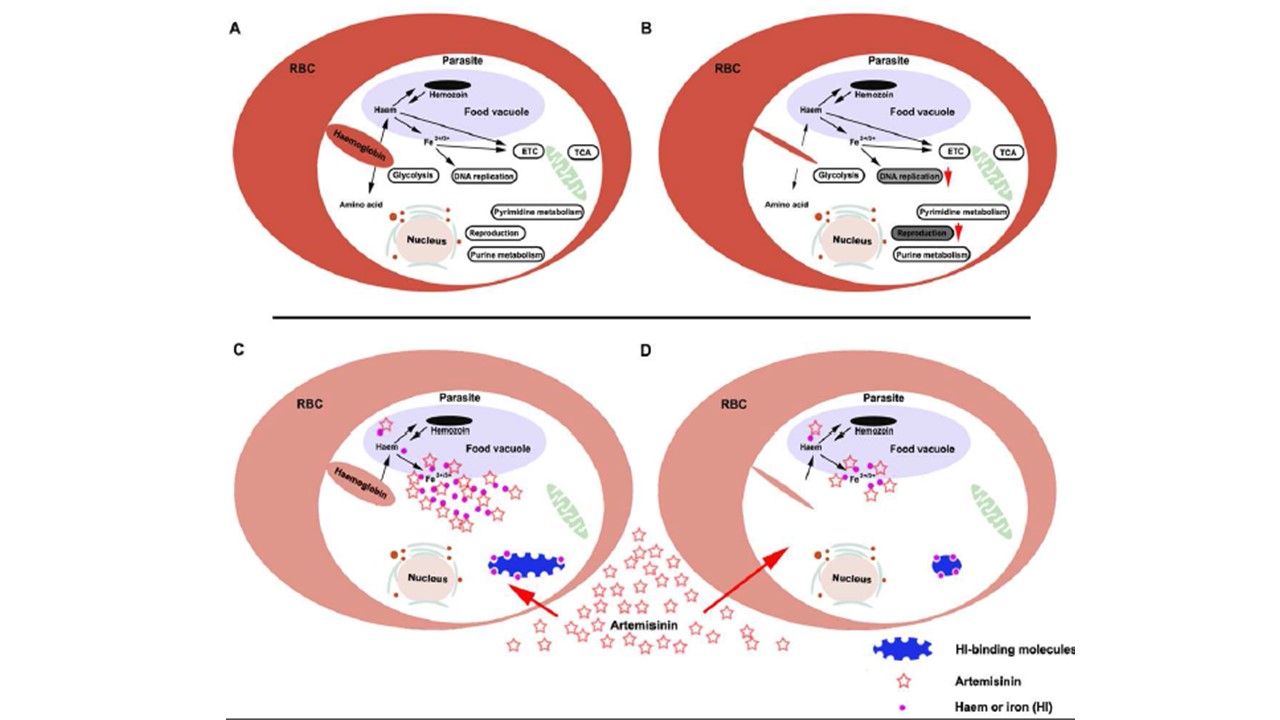
Effect of PfK13 mutation on malaria parasites. (A) The schematic illustrates the primary metabolic pathways following hemoglobin endocytosis in P. falciparum 3D7WT. (B) PfK13 mutation attenuated hemoglobin endocytosis without significantly altering these primary metabolic pathways while decreasing the expression of genes related to reproduction and DNA synthesis. The schematic illustrates the two potential mechanisms of artemisinin resistance resulting from PfK13 mutations. The release of haem and iron (HI) after the endocytosis and digestion of
hemoglobin is well-established. Upon entering parasites, artemisinin is activated by HI and
simultaneously sequesters HI, resulting in two detrimental effects on the parasites: (1) damage inflicting free radicals are generated, and (2) HI deficiency disrupts the function of HI-related
molecules (C). On one hand, PfK13 mutations reduced hemoglobin endocytosis and impaired HI498 mediated artemisinin activation, leading to resistance against artemisinin (D). On the other hand, the reduced HI requirement was easily met by a small amount of iron in the parasite, resulting in
the resistance of parasites to HI deficiency caused by artemisinin (D).
Si W, Zhao Y, Qin X, Huang Y, Yu J, Liu X, Li Y, Yan X, Zhang Q, Sun J. What exactly does the PfK13 C580Y mutation in Plasmodium falciparum influence? Parasit Vectors. 2023 16(1):421. PMID: 37974285