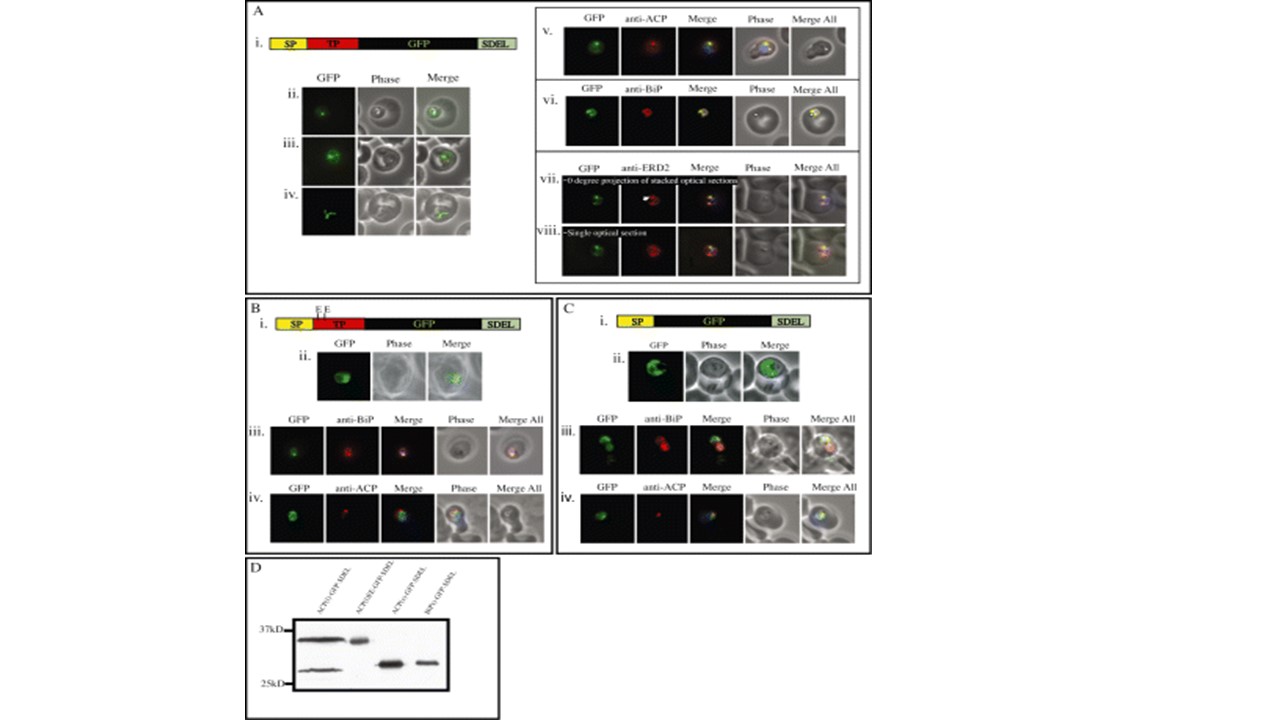
The apicoplast transit peptide is dominant over an SDEL ER retention motif. An SDEL ER retention motif was appended to the end of three apicoplast leader – GFP fusions. A wild-type ACP(l) transit peptide, ACP(l)EE, which contains a mutant transit peptide and ACP(s), which completely lacks a transit peptide. These constructs were designed to test whether the transit peptide or SDEL is recognised first. This competitive experiment allows inference of the position of the apicoplast relative to the cis-Golgi, which houses the SDEL receptor ERD2.Apicoplast targeting was monitored by western blot and fluorescence pattern of GFP.A. (i) Schematic representation of ACP(l)-GFP-SDEL and (ii–viii) localisation of GFP of parasites harbouring this construct. GFP fluorescence shows a typical apicoplast localisation (ii–iv) but additionally in late ring and early trophozoite stage parasites shows fluorescence in a structure typical of the ER (iii). (v–viii) Anti-ACP, anti-BiP and anti-ERD2 IFA’s on ACP(l)-GFP-SDEL expressing parasites assess the location of GFP. A large amount of GFP co-localises with ACP (v) demonstrating apicoplast targeting, whereas the rest of GFP fluorescence co-localises with the ER marker BiP (vi). GFP however, largely is absent from the cis-Golgi (vii – arrowhead) as ascertained by ERD2 staining(vii–viii). ERD2 localises to the cis-Golgi and also to the ER as it retrieves XDEL containing proteins from the cis-Golgi. Fluorescence from ACP(l)-GFP-SDEL expressing parasites does not overlap with the most intense spot of ERD2 staining (as ascertained by single optical section– viii) suggesting that the apicoplast is not in the cis-Golgi.B. Transgenic parasites were created harbouring ACP(l)EE-GFP-SDEL (i). The pattern of GFP in live parasites was reminiscent of an ER localisation (ii) (van Dooren et al., 2005). All GFP co-localises with anti-BiP (iii) and not with the apicoplast marker ACP (iv).C. Transgenic parasites expressing ACP(s)-GFP-SDEL (i). ACP(s)-GFP-SDEL has a typical ER localization in live parasites (ii), which also colocalizes with anti-BiP (iii) and not with anti-ACP (iv).D. A western blot of parasites expressing ACP(l)-GFP-SDEL, ACP(l)EE-GFP-SDEL, ACP(s)-GFP-SDEL and BiP(s)-GFP-SDEL (van Dooren et al., 2005). ACP(l)-GFP-SDEL is processed and infers apicoplast targeting whereas ACP(l)EE-GFP-SDEL and ACP(s)-GFP remain unprocessed which confirms the microscopy observations that GFP does not enter the apicoplast when the transit peptide is ineffectual orabsent. Tonkin CJ, Struck NS, Mullin KA, Stimmler LM, McFadden GI. Evidence for Golgi-independent transport from the early secretory pathway to the plastid in malaria parasites. Mol Microbiol. 2006 61(3):614-30. PMID: 16787449.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0208500 | acyl carrier protein |
| PF3D7_0917900 | PfHsp70-2 |