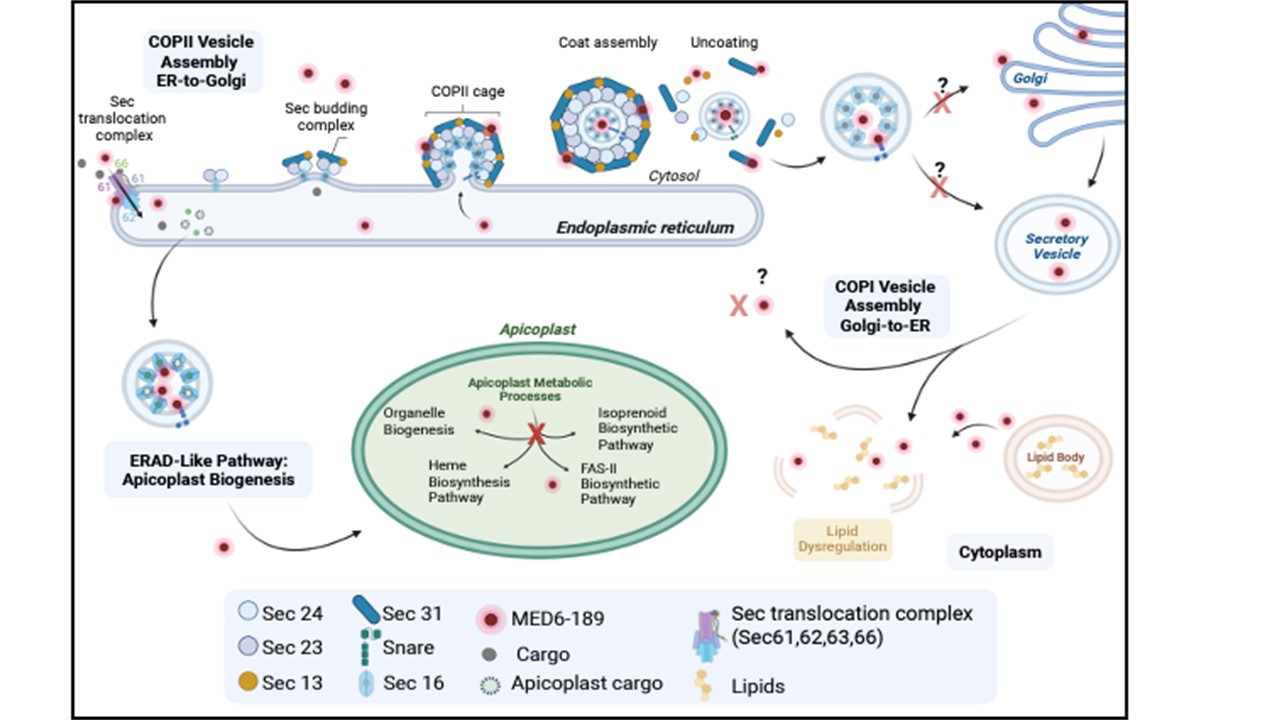
Proposed mode of action of MED6-189 in P. falciparum-infected erythrocytes. The compound is imported into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via the Sec translocation complex (SEC61,62,63,66), where it interacts with components of the ER transport machinery. The compounds translocated into the apicoplast where it directly interacts with proteins involved in crucial apicoplast function, ultimately disrupting this vital organelle. The interactions of MED6-189 with components of the apicoplast function and trafficking systems lead to dysregulation of lipids, resulting in the disruption of key biological processes within the Plasmodium parasite. Chahine Z et alkalihinol analog disrupts apicoplast function and vesicular trafficking in P. falciparum malaria. Science. 2024 PMID: 39325875. Chahine Z, et al A Potent Kalihinol Analogue Disrupts Apicoplast Function and Vesicular Trafficking in P. falciparum Malaria. bioRxiv 2023 PMID: 38045341
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0214100 | protein transport protein SEC31 |
| PF3D7_0822600 | protein transport protein SEC23 |
| PF3D7_1230700 | protein transport protein SEC13 |