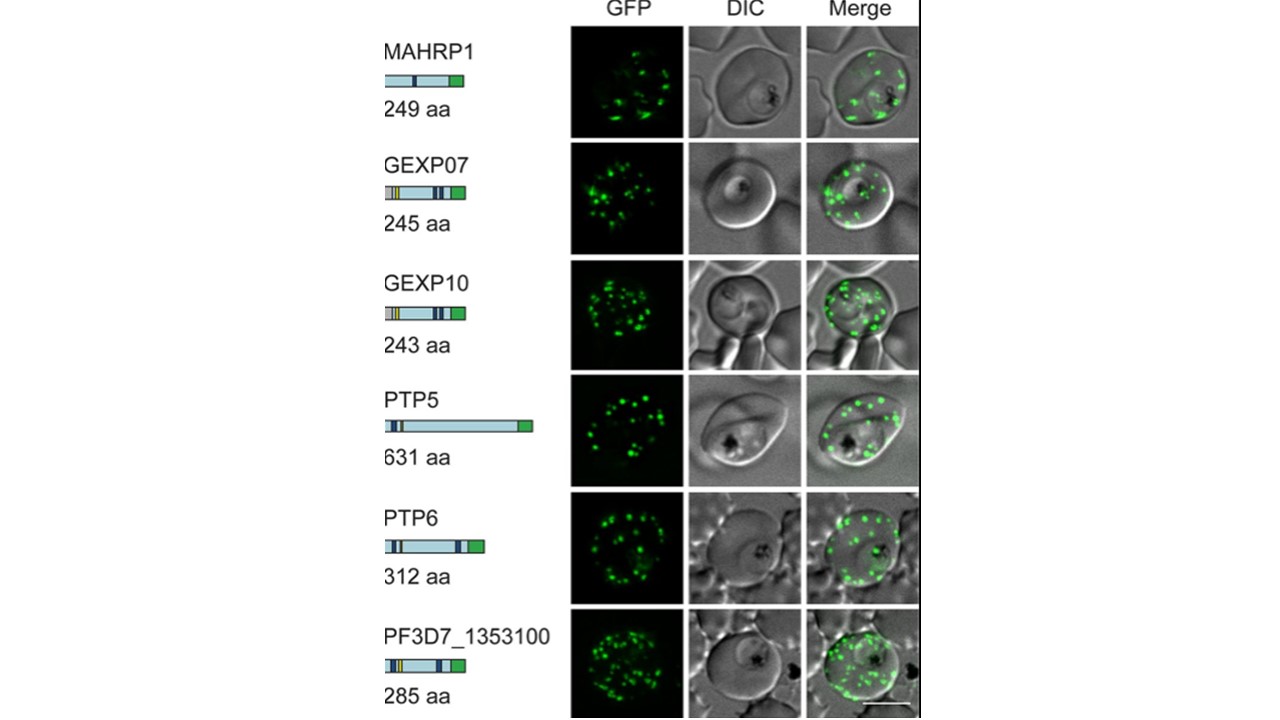
Live-cell fluorescence analysis of GFP-tagged exported proteins. Predicted native protein lengths (amino acids [aa]) and schematic representations of six proteins that were selected for GFP tagging are shown on the left. Gray = signal sequence, blue = transmembrane domain (TM), yellow = PEXEL motif, green = GFP tag. Live-cell fluorescence and DIC microscopy of transfectants expressing GFP-tagged putative Maurer’s cleft proteins revealed fluorescent puncta in the RBC cytoplasm. Scale bar = 5 μm. Disruption of GEXP07 causes Maurer's cleft fragmentation, aberrant knobs, ablation of PfEMP1 surface expression, and loss of the PfEMP1-mediated adhesion. ΔGEXP07 parasites have a growth advantage compared to wild-type parasites, and the infected RBCs are more deformable and more osmotically. McHugh E, Carmo OMS, Blanch A, Looker O, Liu B, Tiash S, Andrew D, Batinovic S, Low AJY, Cho HJ, McMillan P, Tilley L, Dixon MWA. Role of Plasmodium falciparum Protein GEXP07 in Maurer's Cleft Morphology, Knob Architecture, and P. falciparum EMP1 Trafficking. mBio. 2020 11(2):e03320-19. PMID: 32184257
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0113900 | Plasmodium exported protein (hyp8) |
| PF3D7_1002100 | EMP1-trafficking protein |
| PF3D7_1302000 | EMP1-trafficking protein |
| PF3D7_1353100 | Plasmodium exported protein, unknown function |