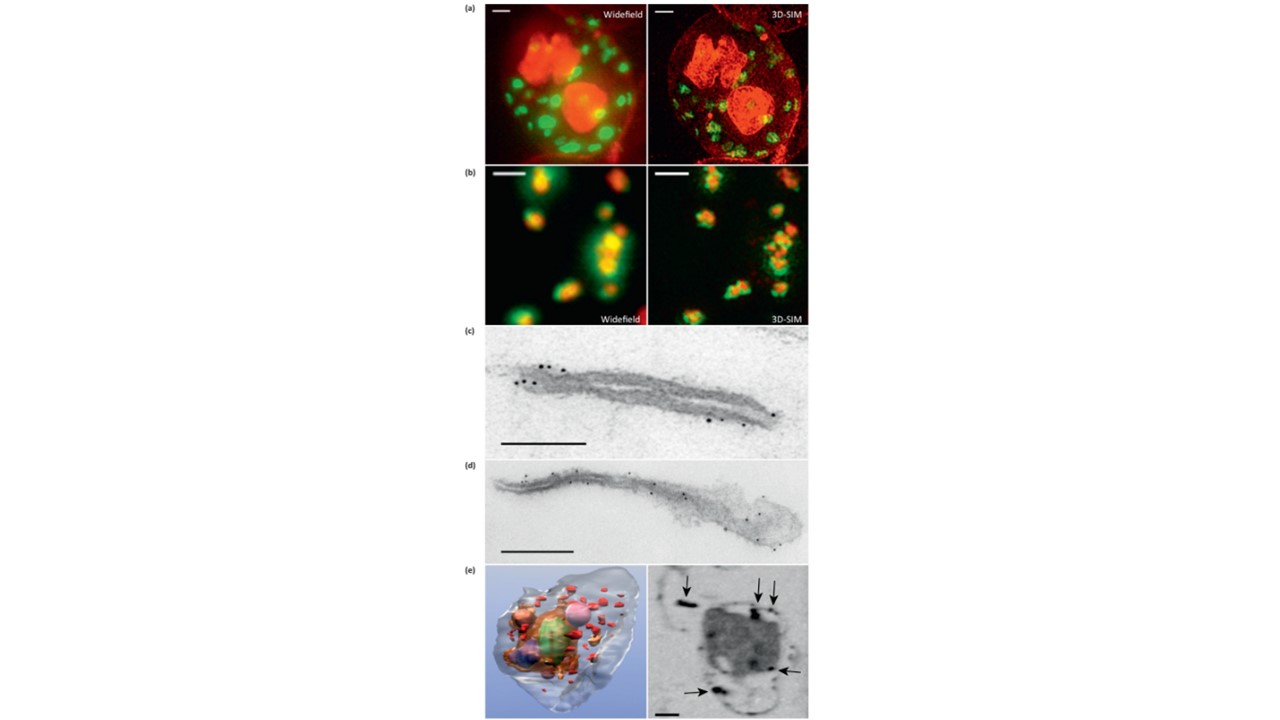
Microscopy methods for localizing Plasmodium falciparum Maurer’s cleft-associated proteins. (a) Plasmodium falciparum transfectants expressing REX1-GFP (green) co-stained with a membrane stain (red) and imaged using conventional widefield fluorescence microscopy and 3D structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM). Scale bars = 1 mm. (b) Immunofluorescence microscopy of P. falciparum REX1-GFP transfectants labeled with anti-GFP (green) and anti-MAHRP1 (red) antibodies. The sample was imaged using conventional widefield fluorescence microscopy and 3D-SIM. Scale bars = 1 mm. (c, d) Immunoelectron microscopy. Red blood cells (RBCs) infected with trophozoite stage REX1-GFP transfectants [(c) scale bar = 100 nm)] or MAHRP1-GFP transfectants [(d) (scale bar = 200 nm)] were permeabilized with Equinatoxin II and labeled with anti-GFP antiserum followed by 6 nm gold-labeled protein A. (e) Left hand panel: rendered cryo-X-ray tomogram of an Equinatoxin II-permeabilized trophozoite-infected RBC. The surface of the trophozoite is rendered in brown, the nucleus in green, the digestive vacuole in purple. Hemoglobin-containing vesicles in the RBC cytoplasm are rendered in magenta and Maurer’s clefts in red. Right hand panel: cryo-X-ray micrograph of an infected RBC. MAHRP1-GFP transfectant-infected RBCs were permeabilized and labeled with mouse anti-GFP antiserum followed by 6 nm gold-labeled protein A. The size of the gold particles was increased by silver enhancement. Dark deposits in the RBC cytoplasm (arrowheads) reveal labeling of the Maurer’s clefts. Scale bars = 500 nm. Woodcroft BJ, McMillan PJ, Dekiwadia C, Tilley L, Ralph SA. Determination of protein subcellular localization in apicomplexan parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2012 28(12):546-54. PMID: 22995720.