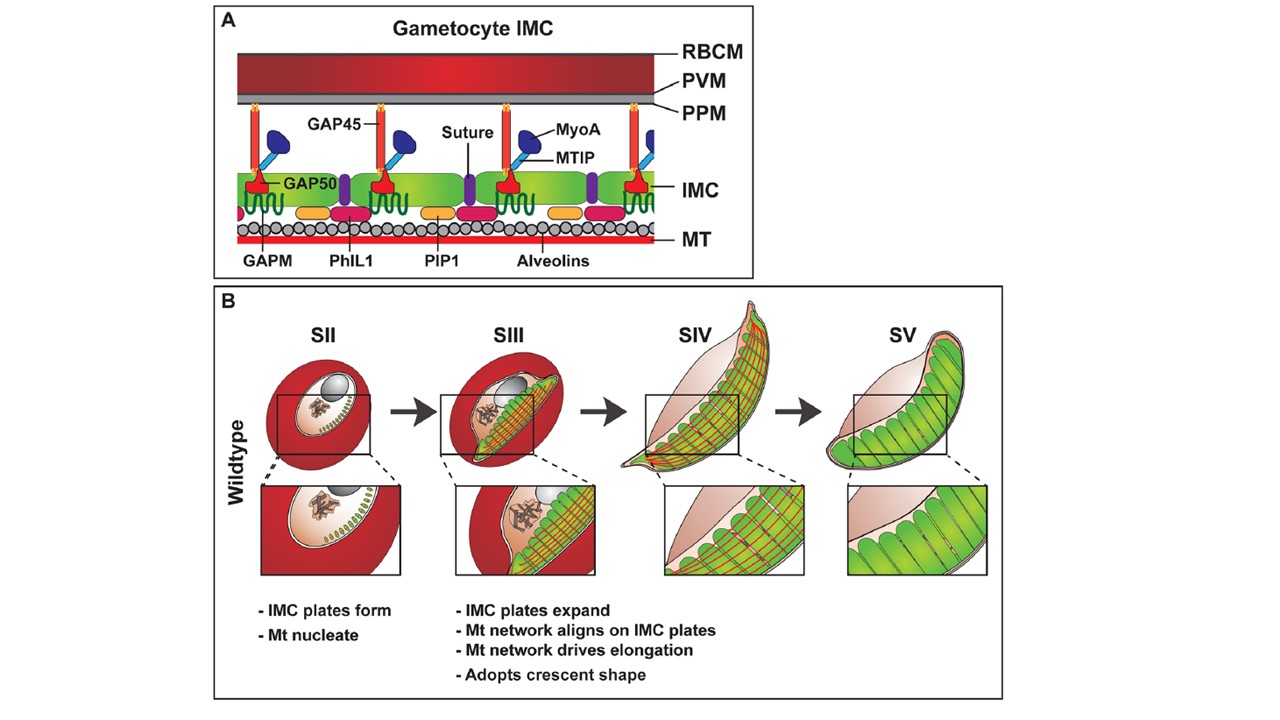
Model and schematic of the gametocyte IMC development. (A) Schematic showing the proposed positioning of proteins in the gametocyte IMC. Red blood cell membrane (RBCM); Parasitophorous vacuole membrane (PVM); parasite plasma membrane (PPM); inner membrane complex (IMC); microtubules (MT); Photosensitized 5-[125I] iodonaphthalene-1-azide labeled protein-1 (PhIL1); PhIL1-interacting protein 1 (PIP); Glideosome-associated protein 45 and 50 (GAP45 and 50); Glideosome-associated protein with multiple membrane spans (GAPM); myosin-A (MyoA); myosin-A tail domain interacting protein (MTIP). (B) Proposed model of plate formation and expansion during development and elongation of wild type gametocytes. IMC plates are deposited as 13 disk-like structures on the cytoplasmic side of the parasite plasma membrane. These plates act as a scaffold for microtubule formation. As the parasite develops, the plates expand through the addition of new membrane to the leading edges of the plates. The microtubule network aligns on these plates and drives parasite elongation. These plates continue to develop through to stage IV of development. At stage V, the microtubule network is disassembled but the IMC remains at the parasite periphery.
Parkyn Schneider M, Liu B, Glock P, Suttie A, McHugh E, Andrew D, Batinovic S, Williamson N, Hanssen E, McMillan P, Hliscs M, Tilley L, Dixon MWA. Disrupting assembly of the inner membrane complex blocks Plasmodium falciparum sexual stage development. PLoS Pathog. 2017 13(10):e1006659. PMID: 28985225