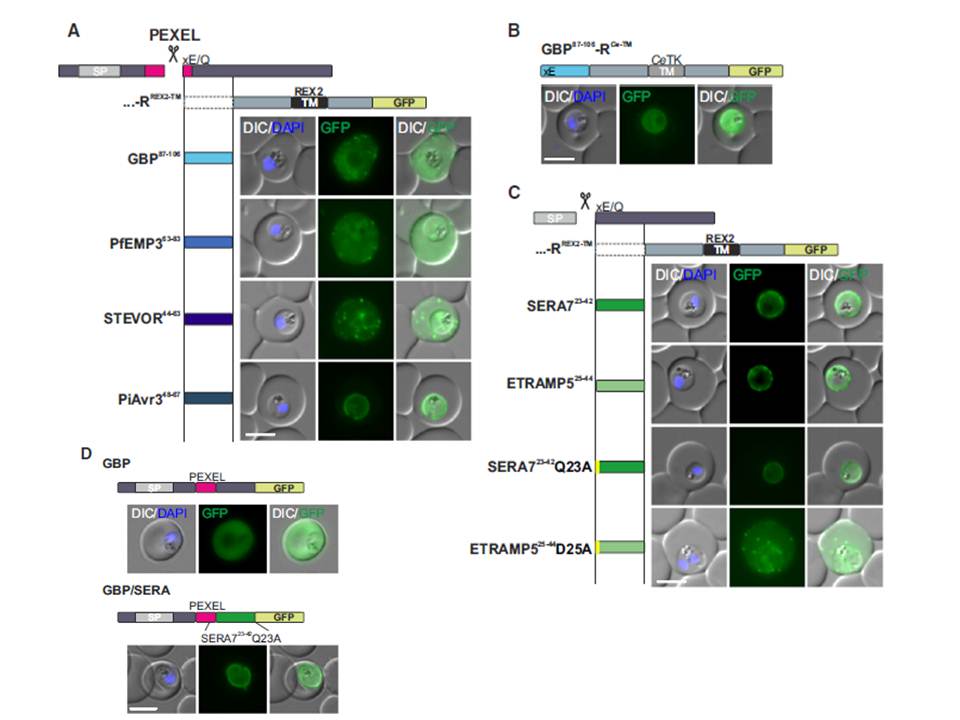
Mature PEXEL N Termini Promote Export of RREX2-TM (A–C) Images of live P. falciparum parasites expressing RREX2-TM fused with the mature N termini of PEXEL proteins (A), GBP87–106-RCe-TM (B), or RREX2-TM fused with the mature N termini of nonexported secretory proteins (C). The position of the appended region in the original protein is shown above each panel.
(D) Images of live P. falciparum parasites expressing truncated GBP fused to GFP (GBP, top) or GBP-GFP with the mature N terminus of SERA7Q23A after the PEXEL (GBP/SERA, bottom). Although these N termini contain only the last of the conserved PEXEL residues (PEXEL position 5) and the nonconserved position 4, they promoted export of the reporter into the host cell (A). GFP fluorescence was detected in the erythrocyte cytosol and the Maurer’s clefts.
Grüring C, Heiber A, Kruse F, Flemming S, Franci G, Colombo SF, Fasana E,
Schoeler H, Borgese N, Stunnenberg HG, Przyborski JM, Gilberger TW, Spielmann T. Uncovering common principles in protein export of malaria parasites. Cell Host Microbe. 2012 12(5):717-29.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0201900 | erythrocyte membrane protein 3 |
| PF3D7_0207400 | serine repeat antigen 7 |
| PF3D7_0532100 | early transcribed membrane protein 5 |
| PF3D7_0936000 | ring-exported protein 2 |
| PF3D7_1016300 | glycophorin binding protein |