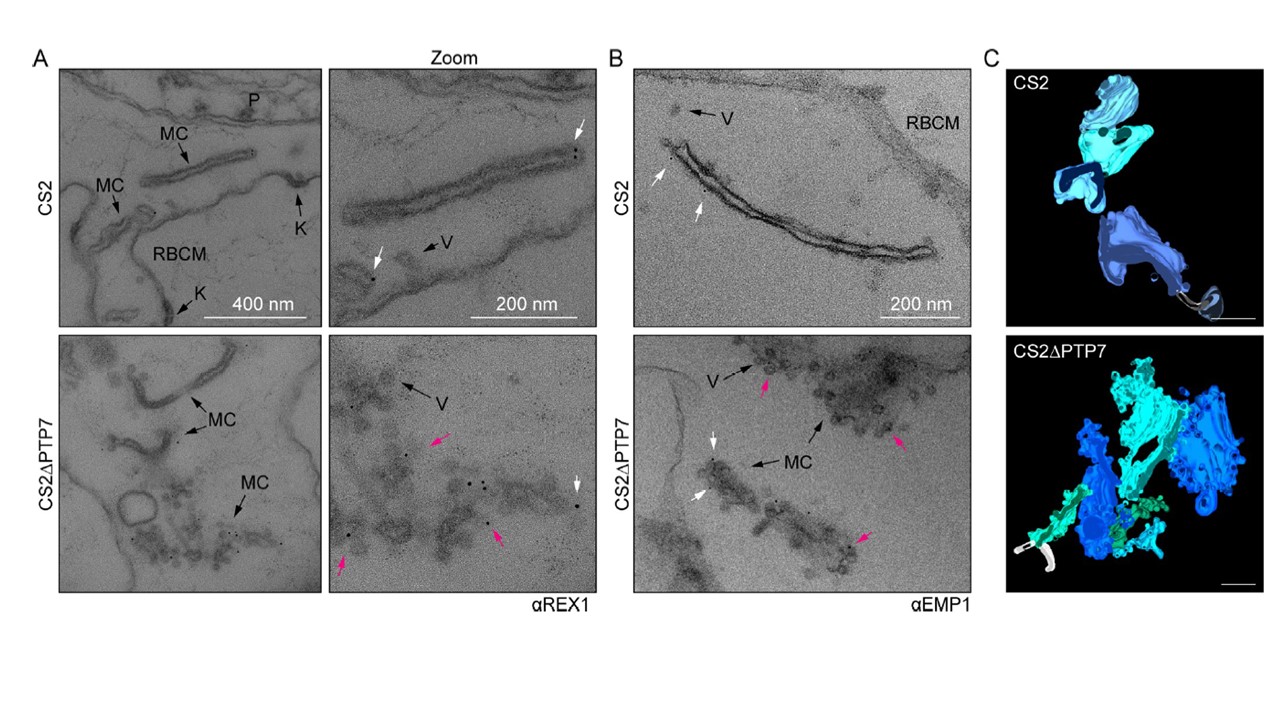
PTP7 disruption leads to an accumulation of vesicles at the clefts. (A-B) Immuno-electron micrographs of 20–32 hpi CS2 and ΔPTP7 infected RBCs permeabilized with Equinatoxin-II and probed for REX1 (A) (αREX1-repeats [63]) or EMP1 (B) (αR3031 [40]) followed by immunogold secondary labeling with protein-A (EM grade, 6 nm gold). K: knob, V: vesicle, MC: Maurer’s cleft, RBCM: red blood cell membrane. (B) Immuno-electron micrographs of αR3031 (EMP1) labeled cells. Magenta arrows: gold labeled puncta, white arrows: gold labeled vesicles. (C) Clefts modeled from tomogram reconstructions of each cell line. Maurer’s clefts, green and blue hues; tethers, white stalks. Scale bar, 200 nm
Carmo OMS, Shami GJ, Cox D, Liu B, Blanch AJ, Tiash S, Tilley L, Dixon MWA. Deletion of the Plasmodium falciparum exported protein PTP7 leads to Maurer's clefts vesiculation, host cell remodeling defects, and loss of surface presentation of EMP1. PLoS Pathog. 2022 18(8):e1009882.
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_0301700 | Plasmodium exported protein, unknown function |