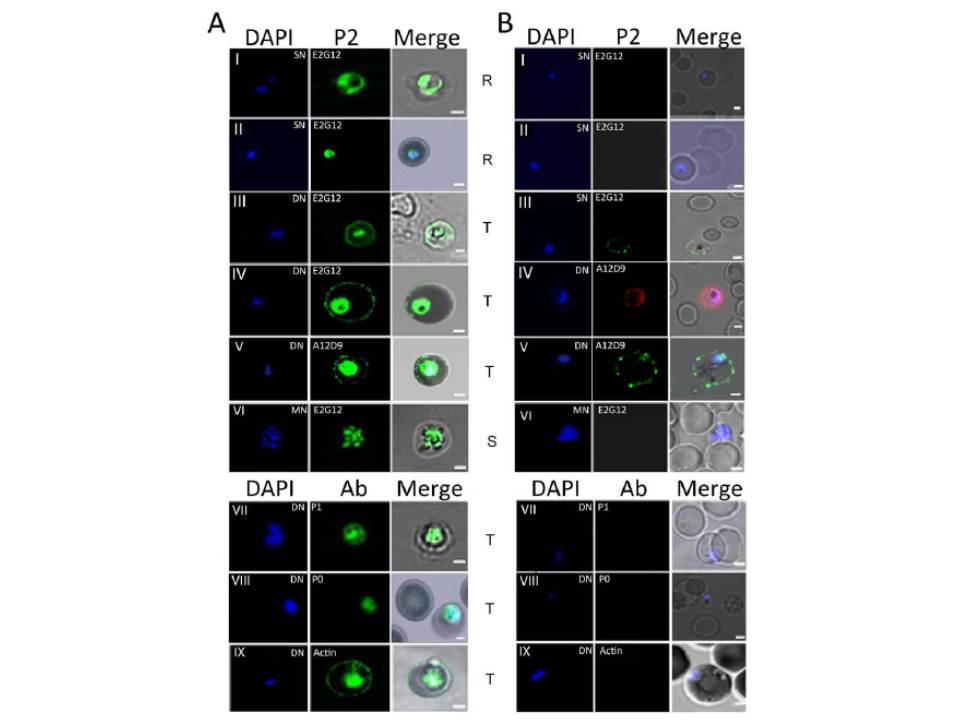
Immunofluorescence assay of P. falciparum infected erythrocytes (IE) using various antibodies. (A) & (B) show confocal images of permiabilized (IFA) and unpermeabilized in solution (SIFA) assays respectively, of different IE stages (I, II: Ring; III, IV, V, VII, VIII, IX: trophozoite; VI: schizont) IFA analysis of permeabilized IEs from asynchronous cultures of P. falciparum 3D7 showed a transient presence of P2 protein on the IE-surface at certain stages of development (A). This was often coincident with a dumbbell shape, elongated or crescent shaped DAPI stained nuclei (henceforth designated as the di-nuclear or DN-stage). It was not seen with the tightly packed single nuclear (SN) rings, nor the multi-nuclear (MN) schizont stage IE-surfaces (A). Cytoplasmic P2 staining was observed at all stages (A). To test for surface exposure, unpermeabilized solution immunofluoroscence assay (SIFA) was carried out which confirmed the presence of P2 on the outer IE surface at the DN stage but not at the SN or MN stages (B). Two different anti-P2 mAbs, E2G12 and A12D9, as well as two different secondary antibodies with different flurophores (Alexa 488 and 594) showed similar results, confirming the specific surface reactivity of PfP2 protein.
Das S, Basu H, Korde R, Tewari R, Sharma S. Arrest of Nuclear Division in Plasmodium through Blockage of Erythrocyte Surface Exposed Ribosomal Protein P2. PLoS Pathog. 2012 Aug;8(8):e1002858.