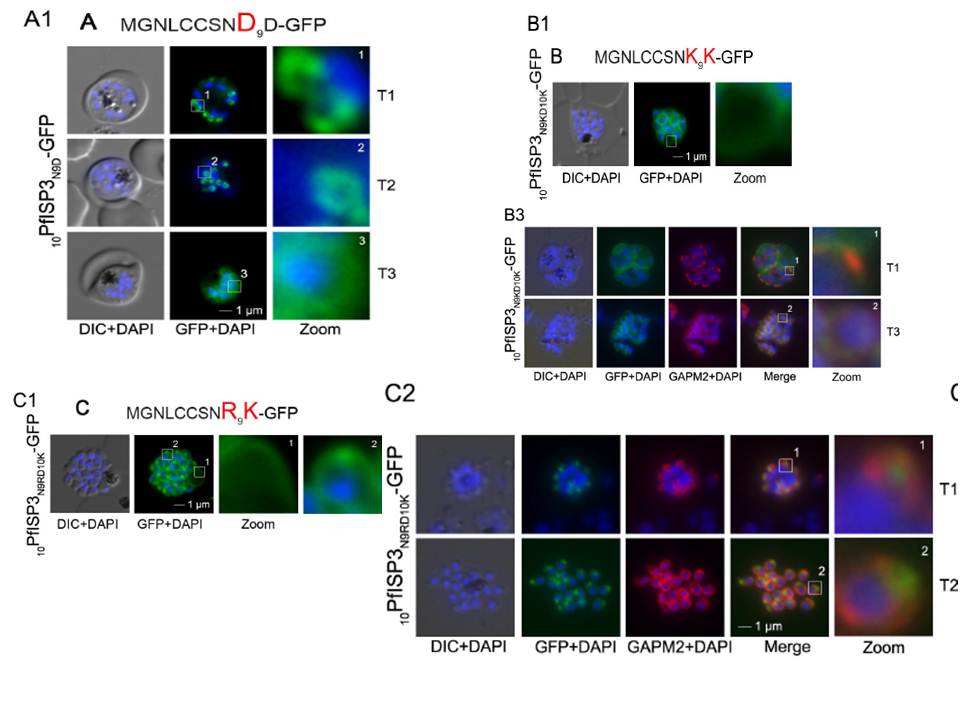
Re-direction of the IMC 10PfISP3-GFP fusion protein to the rhoptry membrane. A. Substitution of N9 with D (10PfISP3N9D-GFP, A) does not interfere with correct IMC recruitment of the GFP-fusion protein (A1). Nuclei stained with DAPI (blue). B-C. The substitution of N9 and D10 with lysine and its expression in the parasite (10PfISP3N9KD10K-GFP) leads to a peripheral localization (B1). The zoom highlights the additional association of this mutant protein with the food vacuole membrane. B2. Western blot analysis using anti-GFP antibodies. B3 Co-localization with the IMC marker GAPM2. Nascent IMC (anti-GAPM2, red) is clearly distinguishable from the peripheral associated 11PfISP1D11K-GFP in early stages (T1) and congruent in late stages (T3). C. In contrast, the substitution of N9 with arginine (10PfISP3N9RD10K-GFP) re-directs the fusion protein to cell periphery (zoom 1) and the apical pole (zoom 2). C2. Co-localization with the rhoptry marker RALP (anti-RALP, red) in fixed cells confirmed PfDHHC1-GFP IMC localization shown here in an early stage of TMC biogenesis (T1).
Wetzel J, Herrmann S, Swapna LS, Prusty D, Peter AT, Kono M, Saini S, Nellimarla S, Wong TW, Wilcke L, Ramsay O, Cabrera A, Biller L, Heincke D, Mossman K, Spielmann T, Ungermann C, Parkinson J, Gilberger TW. The role of palmitoylation for protein recruitment to the inner membrane complex of the malaria parasite. J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 25. PMID:
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_1460600 | inner membrane complex sub-compartment protein 3 |