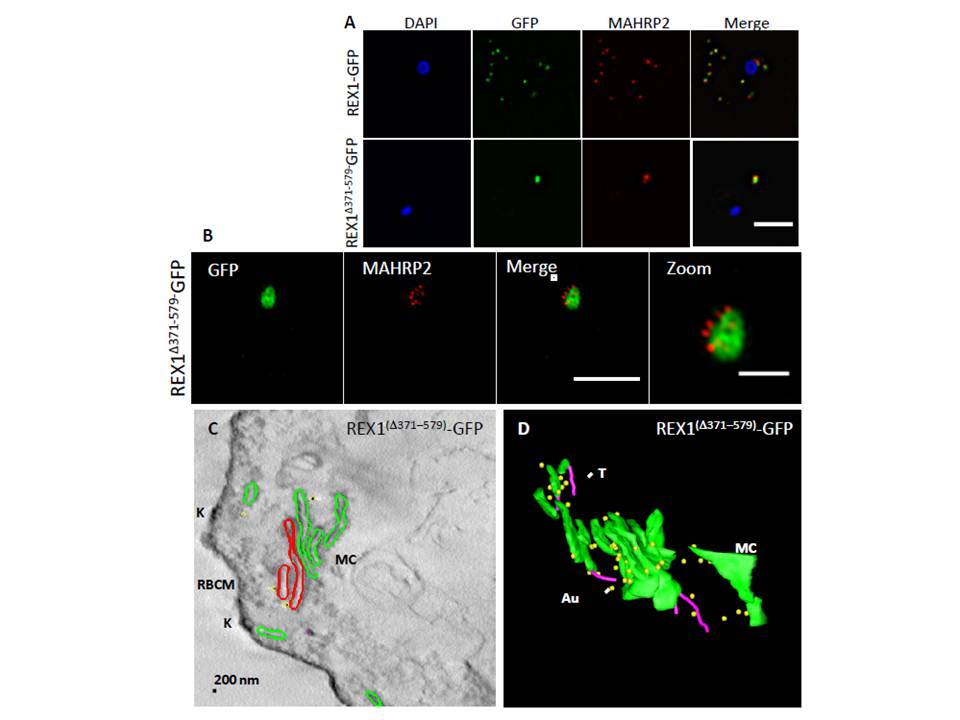
Analysis of the Maurer’s clefts ultrastructure and distribution of tethers of
REX1(Δ371–579)-GFP parasites. REX1-GFP and REX1(Δ371–579)-GFP transfectants were fixed with paraformaldehyde/ glutaraldehyde, permeabilized with Triton X-100, and probed with anti-GFP (green) and anti-MAHRP2 (red). Samples imaged using (A) widefield deconvolution microscopy or (B) 3D-SIM. Scale bars = 3 μm; zoom bar = 1 μm. C. STEM tomogram (600 nm section) of an EqII-permeabilized REX1(Δ371–579)-GFP-infected RBC showing the stacked Maurer’s clefts (MC) layers, and knobs (K) on the RBC membrane (RBCM). The lamella indicated in red share a membrane continuum. D. Rendered STEM tomogram of REX1(Δ371–579)-GFP-infected RBC labelled with anti-GFP antibodies and protein A gold showing Maurer’s clefts (MC, green), tethers (T, magenta) and gold particles (Au, yellow). In REX1-GFP parasites, immunofluorescence reveals MAHRP2 labelling (Fig. 6A) closely adjacent to the REX1-GFP labelled Maurer's clefts. For the REX1Δ371-579-GFP parasites, the MAHRP2 labelling partly overlaps with and partly sits outside the single puncta of GFP labelling.
McHugh E, Batinovic S, Hanssen E, McMillan PJ, Kenny S, Griffin MD, Crawford S, Trenholme KR, Gardiner DL, Dixon MW, Tilley L. A repeat sequence domain of the ring-exported protein-1 of Plasmodium falciparum controls export machinery architecture and virulence protein trafficking. Mol Microbiol. 2015 Aug 24. [Epub ahead of print]
Other associated proteins
| PFID | Formal Annotation |
|---|---|
| PF3D7_1353200 | membrane associated histidine-rich protein 2 |