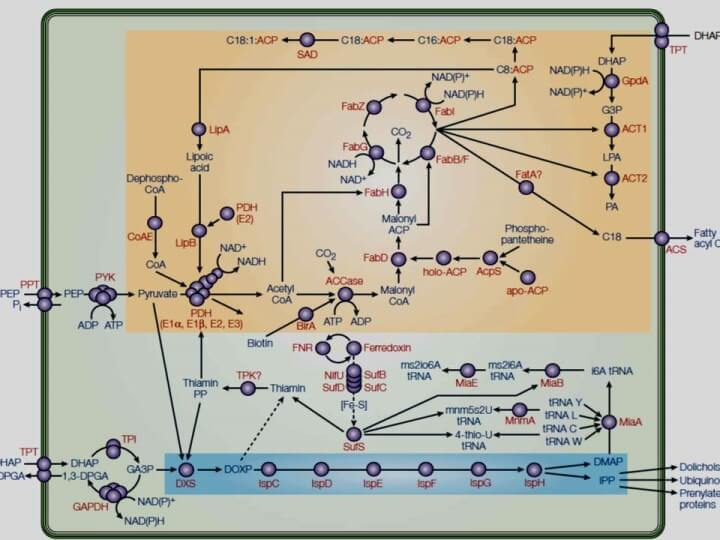
Malaria Parasite Metabolic Pathways
- Home
- Introduction
- MPMP Tutorial New
- MAPS
- Search
- Contact Us
-
Quick Navigation …
Latest Updates
Last update: 07/04/2024
-
07/04/2024
Export of Proteins Protein delivery into the PV and the infected host cell. The entry mechanism and initial formation of the PV rely on machineries that are conserved across the phylum . In contrast, the diversity of dense core granule populations among Apicomplexa parasit -
04/04/2024
Translocation and transport pathways Comparison of the vacuolar translocation and transport pathways in Plasmodium. Effector protein translocation is mediated by the PTEX complex. u and r indicate unfolding and refolding steps prior to and after translocation. PF3D7_1105600 PTEX subunit EXP2 -
19/03/2024
Epigenetics and Epitranscriptomics Schematic of epigenetics and epitranscriptomics. Epigenetics includes chemical modifications of DNA and histone proteins. Epitranscriptomics refers to all chemical modifications on RNA. Figure created with BioRender.com. Abbreviations: ?, pseudouridine; n -
19/03/2024
DNA methylation is mediated by DNA methyltransferases Bi-directional synthesis In many prokaryotes two replication forks develop from at the initiation site, each initiation fork traveling in opposite directions as shown here. Thus, what strand is lagging or leading depends on which replication fork you are -
13/03/2024
Merozoite tomograph Cryo-ET with Volta Phase Plate reveals the organization of subcellular organelles in Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. (A) Tomographic slice of a representative merozoite (left) and its 3D annotation showing the apical rings (orange), rhoptries (red), mem -
06/03/2024
Parasitophorous vacuole proteins Validation of parasitophorous vacuole localizationVacuolar residency is most commonly validated by genetic incorporation of protein tags, as opposed to the laborious and time-consuming generation of specific antibodies for immunofluorescence. Proper valid -
05/03/2024
The parasitophorous vacuole (PV) membrane The parasitophorous vacuole (PV) membrane (PVM) (blue) undergoes distinct morphological phases during parasite egress. On completion of schizogony, the merozoites align around the central food vacuole (dark brown) and the parasitophorous vacuole rounds up -
05/03/2024
PLCd1 PH domain; pleckstrin homology (PH) domains of PLCd1 from the plasma membranes Infection of human erythrocytes by the apicomplexan malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum results in endovacuolar uptake of 4 host proteins that reside in erythrocyte detergent-resistant membranes (DRMs). Whether this vacuolar transport reflects selecti -
03/03/2024
Model of lipid and protein uptake into the erythrocyte DIV and the malarial vacuole (A) The erythrocyte membrane contains a variety of phospholipids (PS, PI/PIP2, PE, PG, etc) and raft (stomatin, flotillins) and nonraft (actin, spectrin) proteins, most of which are taken up into DIV membranes. However, PE- and PG-type phospholipids are s -
01/03/2024
Vacuolar secretion pathways Vacuolar secretion pathways in Plasmodium. Effectors and virulence factors follow the general SRP/Sec61-dependent (Signal Recognition Particle/Sec61 translocon) parasitic secretion pathway starting in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and progressing through
-
07/04/2024
Export of Proteins Protein delivery into the PV and the infected host cell. The entry mechanism and initial formation of the PV rely on machineries that are conserved across the phylum . In contrast, the diversity of dense core granule populations among Apicomplexa parasit -
04/04/2024
Translocation and transport pathways Comparison of the vacuolar translocation and transport pathways in Plasmodium. Effector protein translocation is mediated by the PTEX complex. u and r indicate unfolding and refolding steps prior to and after translocation. PF3D7_1105600 PTEX subunit EXP2 -
19/03/2024
Epigenetics and Epitranscriptomics Schematic of epigenetics and epitranscriptomics. Epigenetics includes chemical modifications of DNA and histone proteins. Epitranscriptomics refers to all chemical modifications on RNA. Figure created with BioRender.com. Abbreviations: ?, pseudouridine; n -
19/03/2024
DNA methylation is mediated by DNA methyltransferases Bi-directional synthesis In many prokaryotes two replication forks develop from at the initiation site, each initiation fork traveling in opposite directions as shown here. Thus, what strand is lagging or leading depends on which replication fork you are -
13/03/2024
Merozoite tomograph Cryo-ET with Volta Phase Plate reveals the organization of subcellular organelles in Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. (A) Tomographic slice of a representative merozoite (left) and its 3D annotation showing the apical rings (orange), rhoptries (red), mem -
06/03/2024
Parasitophorous vacuole proteins Validation of parasitophorous vacuole localizationVacuolar residency is most commonly validated by genetic incorporation of protein tags, as opposed to the laborious and time-consuming generation of specific antibodies for immunofluorescence. Proper valid -
05/03/2024
The parasitophorous vacuole (PV) membrane The parasitophorous vacuole (PV) membrane (PVM) (blue) undergoes distinct morphological phases during parasite egress. On completion of schizogony, the merozoites align around the central food vacuole (dark brown) and the parasitophorous vacuole rounds up -
05/03/2024
PLCd1 PH domain; pleckstrin homology (PH) domains of PLCd1 from the plasma membranes Infection of human erythrocytes by the apicomplexan malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum results in endovacuolar uptake of 4 host proteins that reside in erythrocyte detergent-resistant membranes (DRMs). Whether this vacuolar transport reflects selecti -
03/03/2024
Model of lipid and protein uptake into the erythrocyte DIV and the malarial vacuole (A) The erythrocyte membrane contains a variety of phospholipids (PS, PI/PIP2, PE, PG, etc) and raft (stomatin, flotillins) and nonraft (actin, spectrin) proteins, most of which are taken up into DIV membranes. However, PE- and PG-type phospholipids are s -
01/03/2024
Vacuolar secretion pathways Vacuolar secretion pathways in Plasmodium. Effectors and virulence factors follow the general SRP/Sec61-dependent (Signal Recognition Particle/Sec61 translocon) parasitic secretion pathway starting in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and progressing through
Compiled and maintained by
Hagai Ginsburg
This site is graciously hosted by The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
This site is graciously hosted by The Hebrew University of Jerusalem